Kea DHCP
Introduction
Carsten Strotmann
Created: 2025-11-10 Mon 07:05
In this Chapter
- A short history of DHCP
- Basics of DHCPv4
- Reservations
- Shared Subnet
- References
About DHCP
- DHCP is short for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
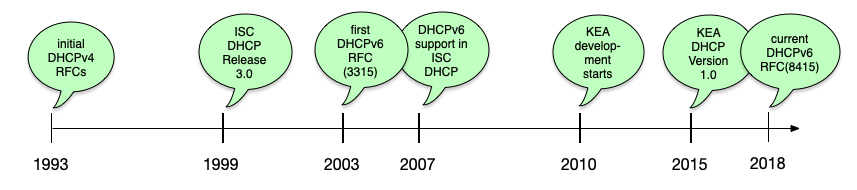
Short history of DHCP (including ISC-DHCP and Kea)
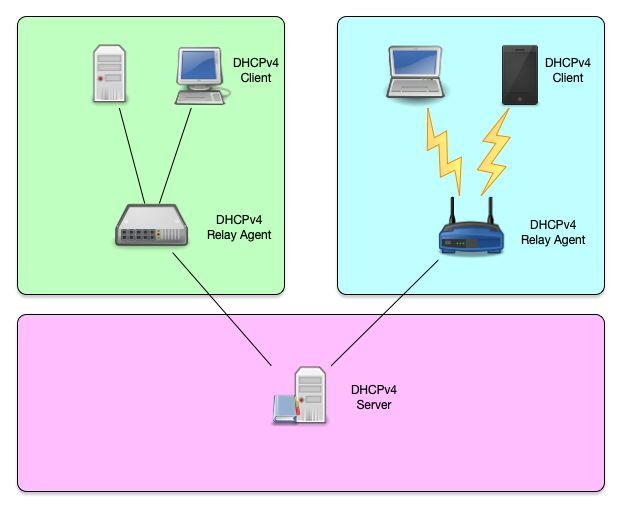
DHCPv4 overview
DHCPv4 overview (1/2)
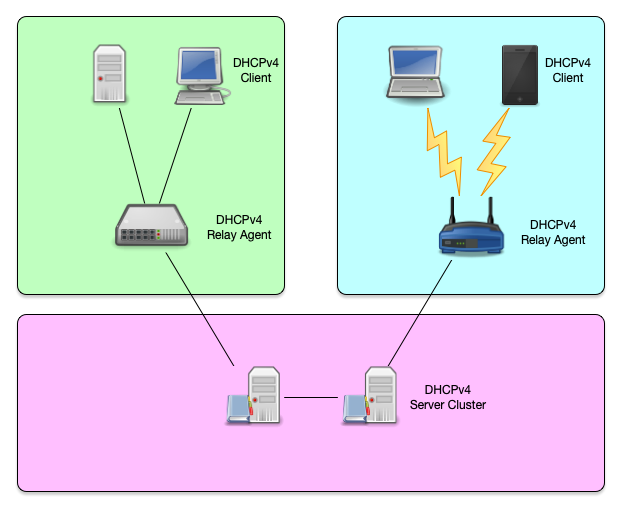
DHCPv4 overview (2/2)
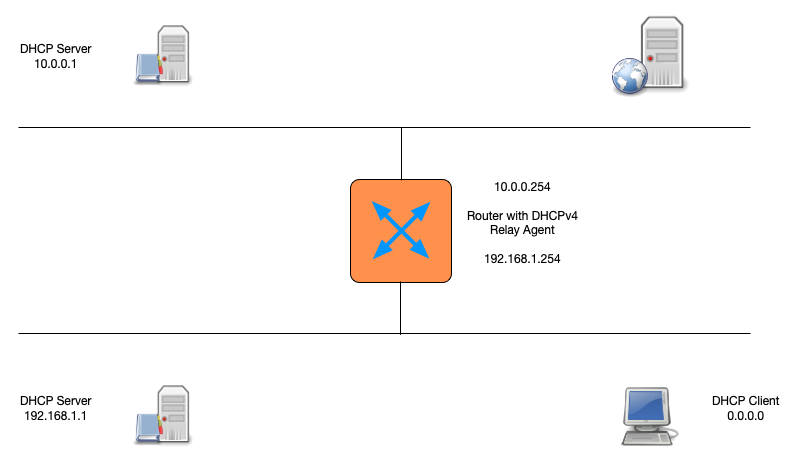
DHCPv4 protocol
- The DHCPv4 protocol uses UDP broadcast and (in some situations)
unicast
- The DHCPv4 server or relay agents listen on port 67
- A DHCPv4 client listens on port 68 for messages from a server or relay agent
- The initial request from a client requires layer 2 (Ethernet) communication
DHCPv4 Lease concept
DHCPv4 Lease (1/3)
- When using the DHCP protocol, a client can never keep an IP Address
forever
- Each IP Address given out by a DHCP server has a "lease" time
- This is the time in seconds that the client is allowed to use the IP Address
DHCPv4 Lease (2/3)
- The "lease" time is delivered in an DHCP option
- It is a 32bit value
- The maximum lease time is $FFFFFFFE (= 4294967294 seconds or ~136 years)
- A lease time of $FFFFFFFF indicates an infinite lease
DHCPv4 Lease (3/3)
- According to the RFC, a DHCP server must store the lease
information to permanent storage before confirming the IP address
to a client
- This can be a performance bottleneck on a DHCP server
DHCP Clients, Relays and Server
- Because a client machine without IP address can only communicate on the local link, the base DHCPv4 protocol is "link-local" only
- DHCPv4 relay-agents can be used to forward DHCPv4 requests to
centralised DHCPv4 server
- DHCP relay-agents are often found in network equipment (e.g. router)
- Dedicated "software based" relay-agents are available

DHCP messages and client server communication
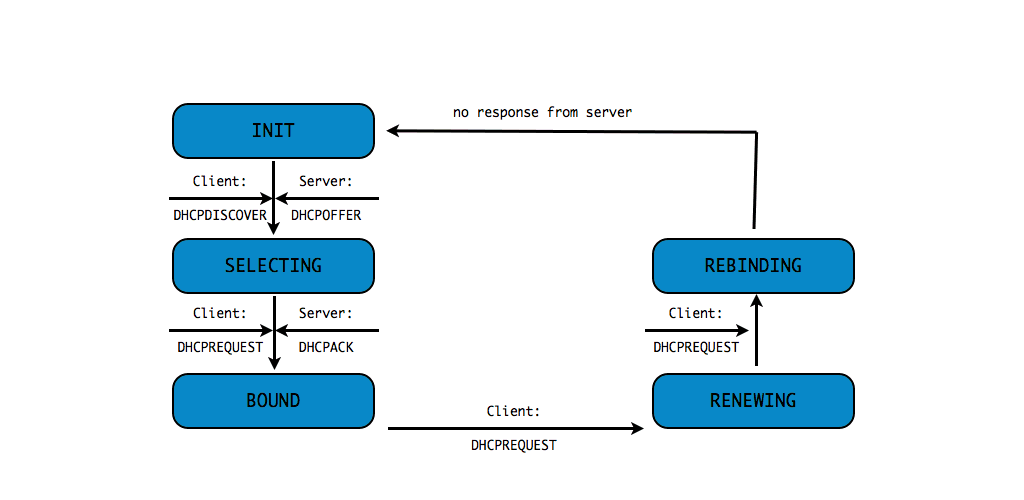
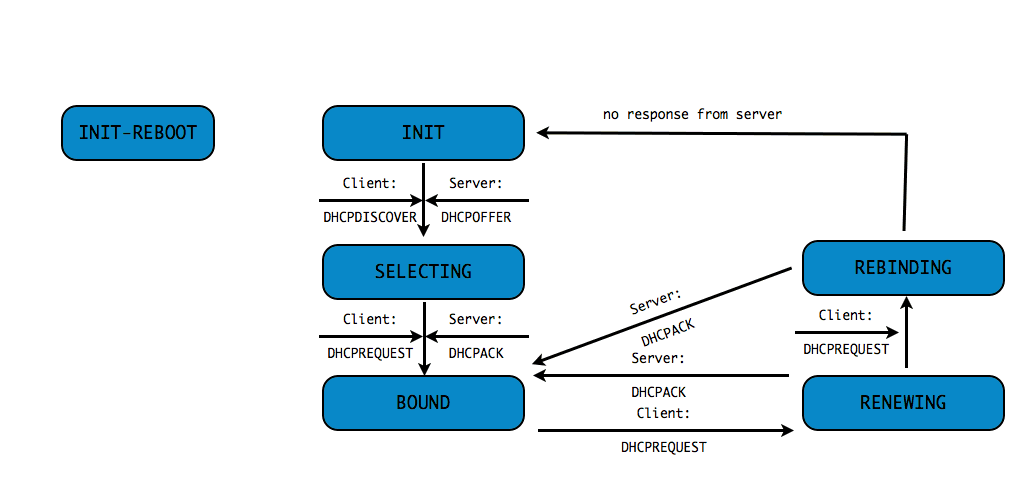
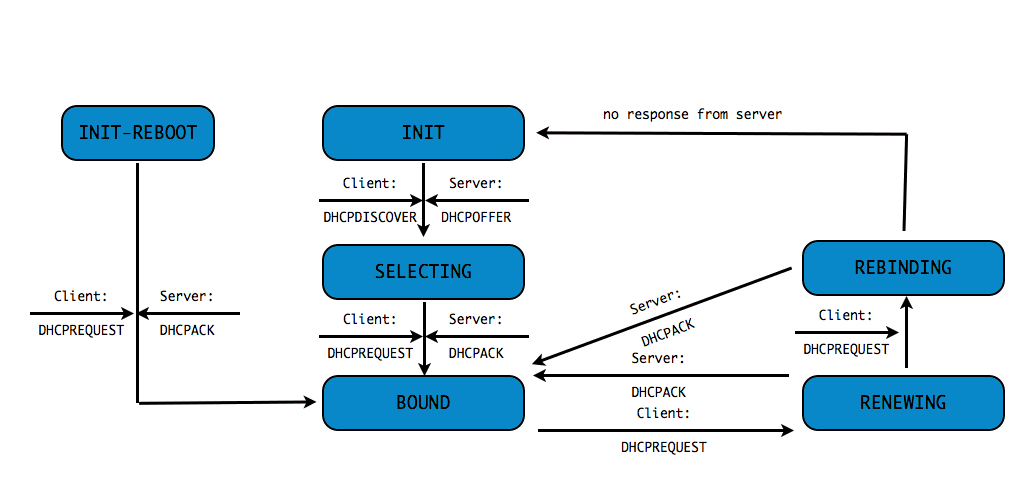
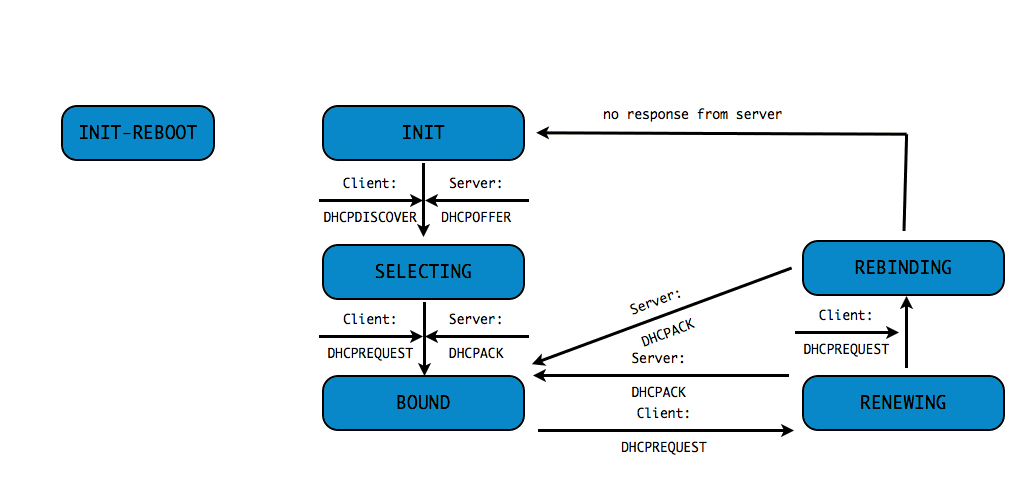
DHCPDISCOVER(client asks: is there a DHCP server that can give me an address)DHCPOFFER(DHCP server offers an address to the client)DHCPREQUEST(client requests the IP address offered by the server)DHCPACK(server marks the IP address as leased and confirms that transaction)
This communication is sometimes called DORA (Discover - Offer - Request - Ack)
DHCP messages (1)
DHCP messages (2)
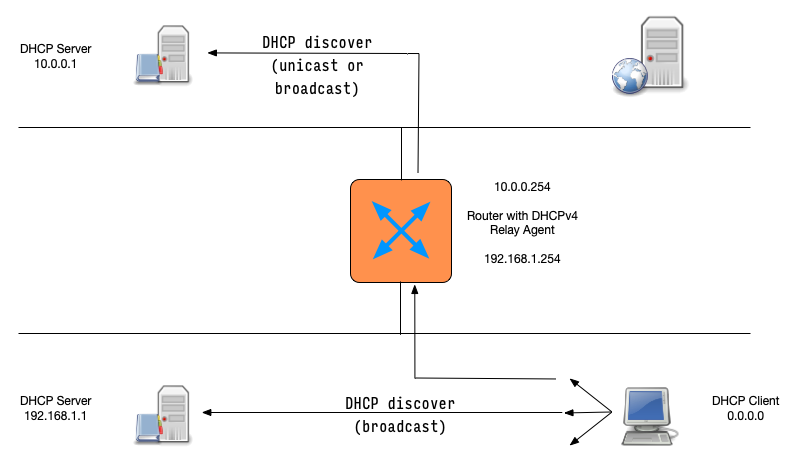
DHCP messages (3)
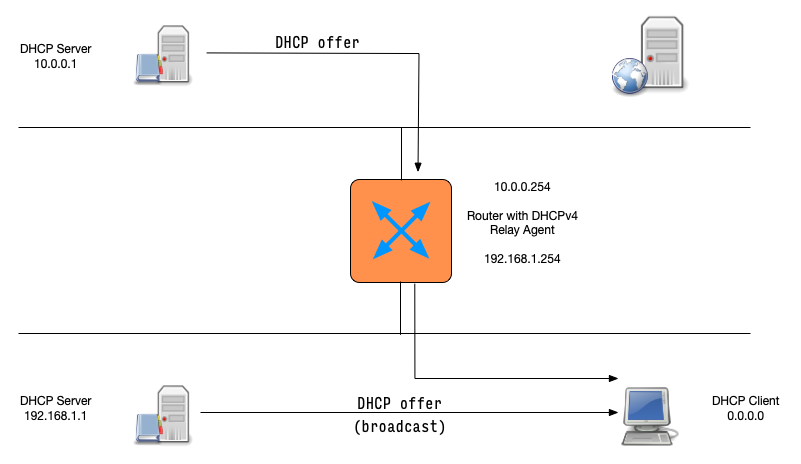
DHCP messages (4)
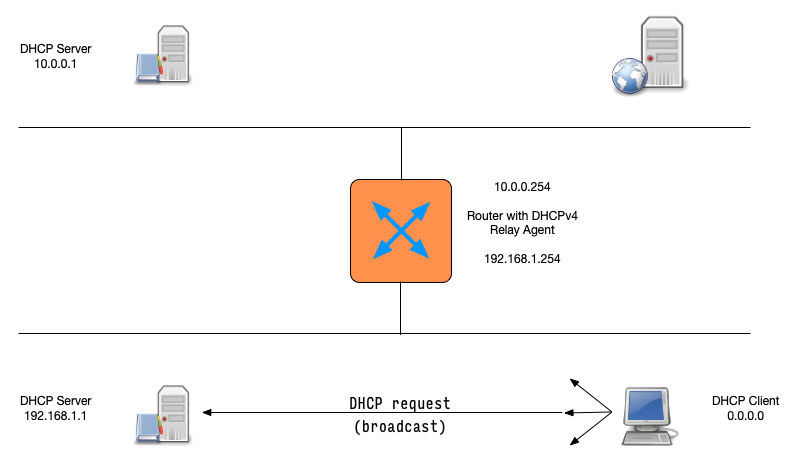
DHCP messages (5)
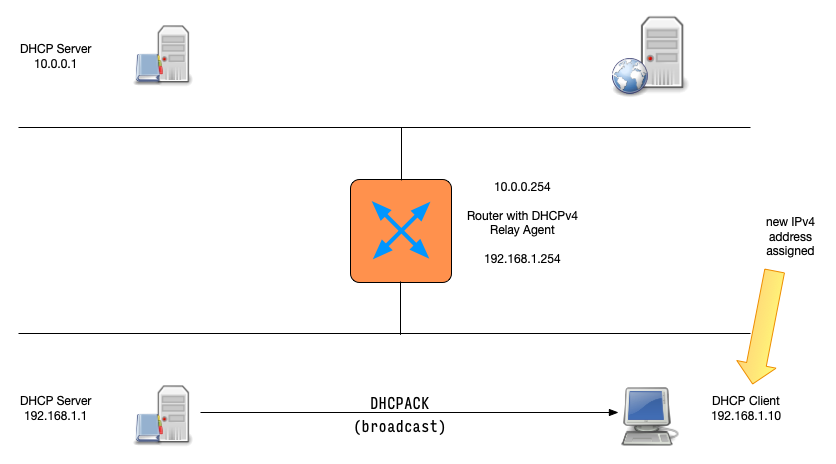
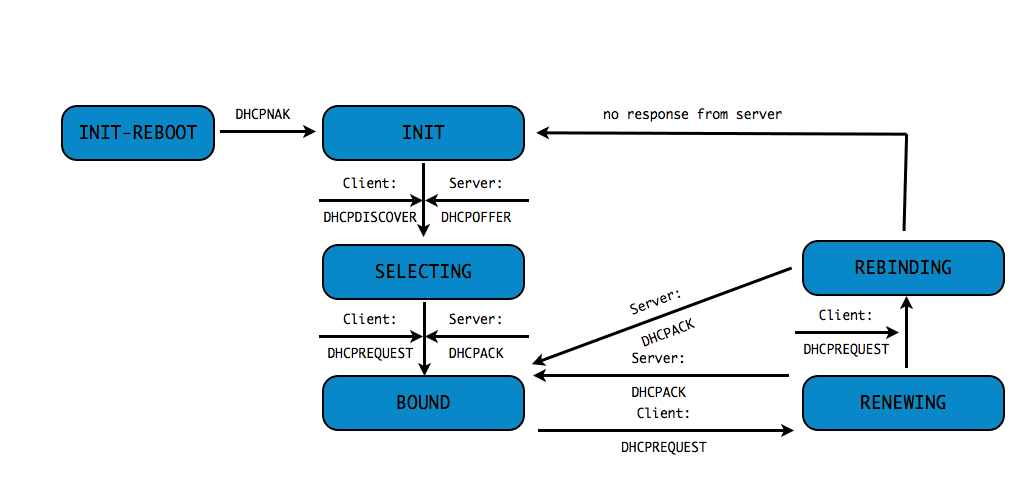
DHCPv4 client states
- A DHCP Client goes through a defined number of "states" when
requesting or renewing a lease
INIT-REBOOT,INIT,SELECTING,BOUND,RENEWING,REBINDING
without IPv4 address (1/10)

without IPv4 address (2/10)
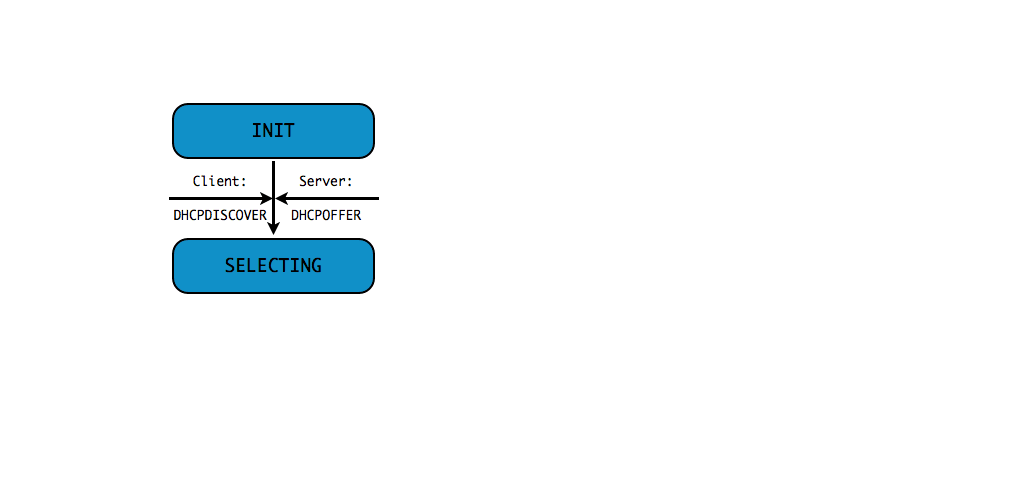
without IPv4 address (3/10)
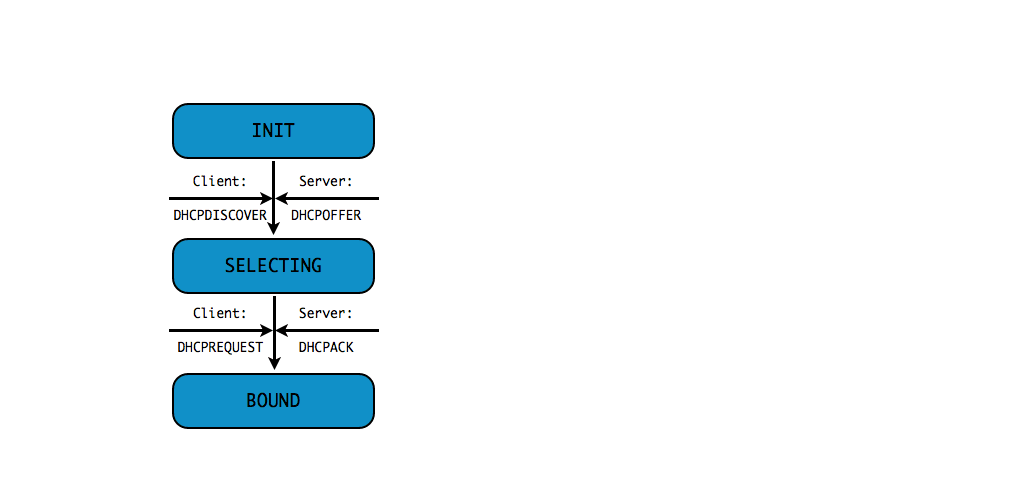
without IPv4 address (4/10)
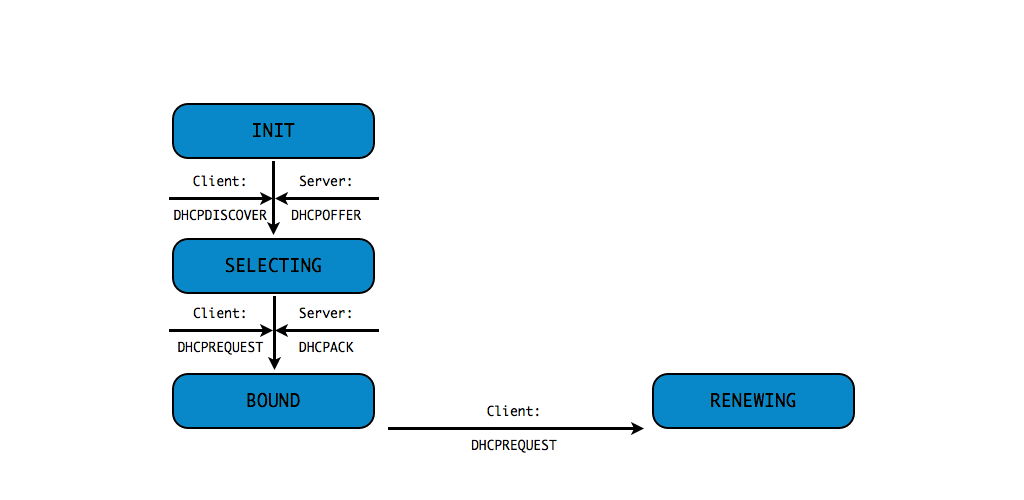
without IPv4 address (5/10)
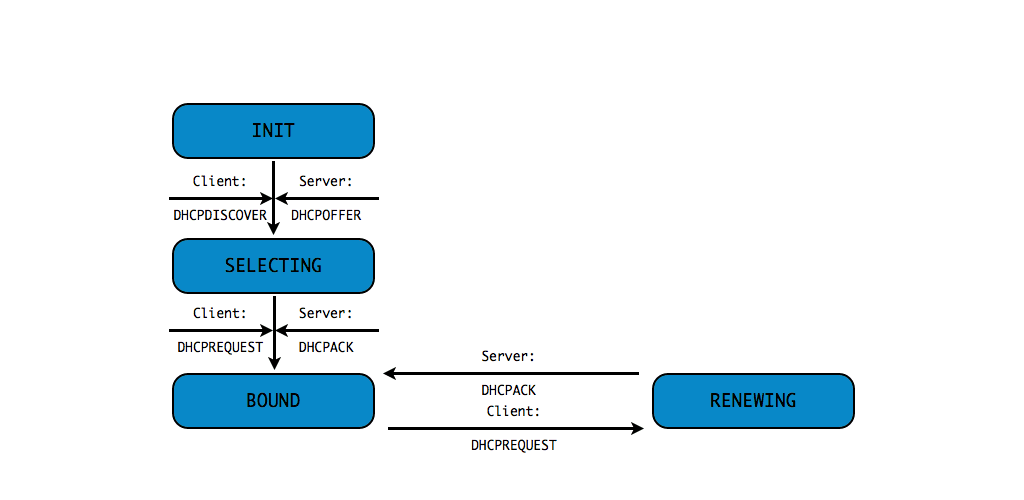
without IPv4 address (6/10)
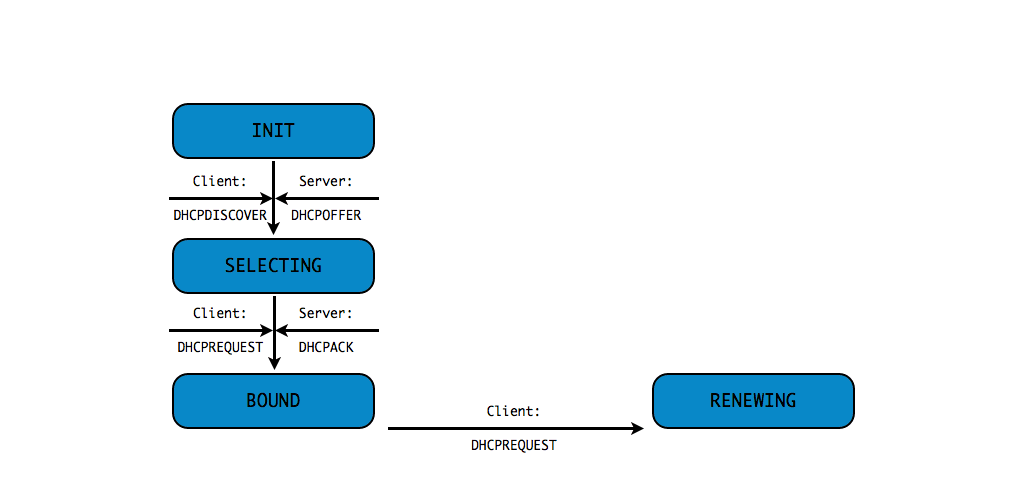
without IPv4 address (7/10)
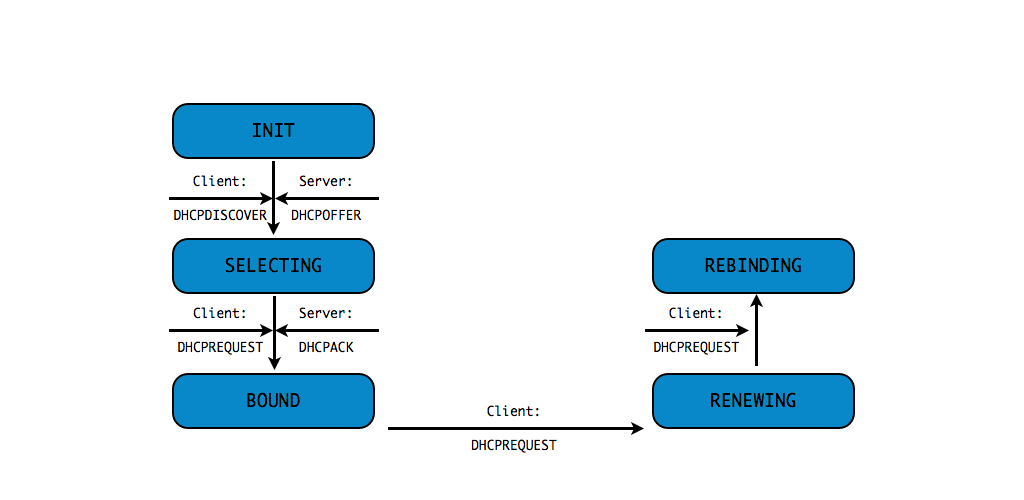
without IPv4 address (8/10)
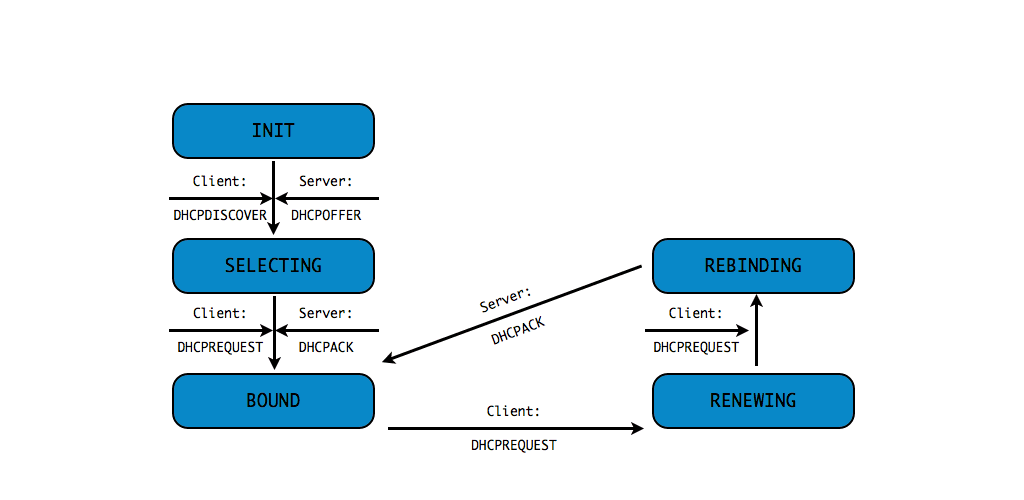
without IPv4 address (9/10)
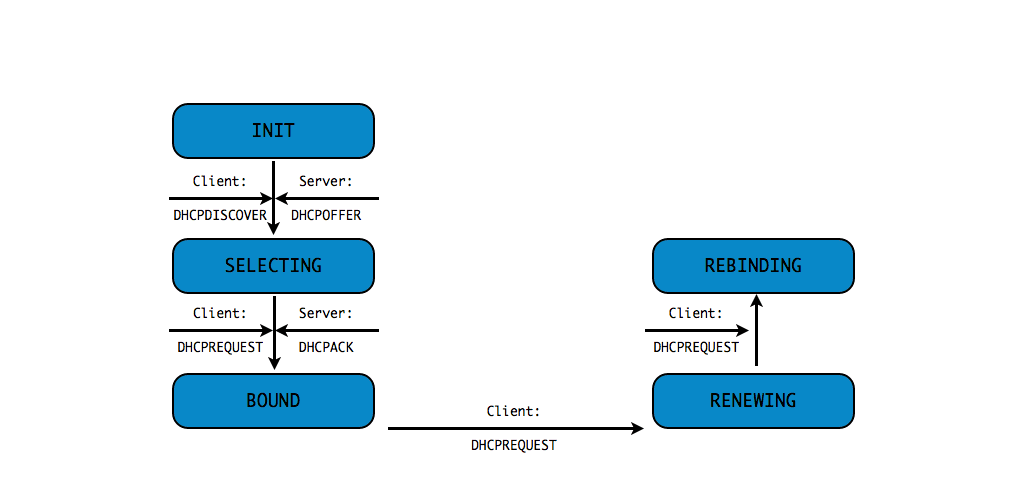
without IPv4 address (10/10)
with IPv4 address (1/4)
with IPv4 address (2/4)
with IPv4 address (3/4)
with IPv4 address (4/4)
Distributing network configuration with DHCP
BOOTP fields and DHCPv4 Options
- In addition to an IP address, DHCPv4 can be used to network
configuration to a client
- BOOTP configuration fields like
next-serverorboot-file-name - DHCPv4 options like
domain-name-serversordomain-search
- BOOTP configuration fields like
Host reservations
Host reservation (1/3)
- Sometimes a DHCP IP address should always be given to the same
DHCP client machine
- For example if that machine receives incoming connections (web-server, printer, database)
- Or if firewall rules define a security policy based on the IP address
- A host reservation binds a DHCP client via a client identifier (Ethernet MAC address) to an IP address
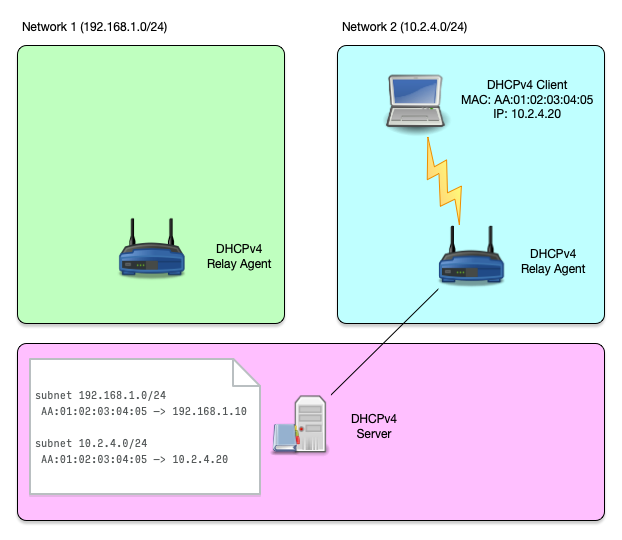
Host reservation (2/3)
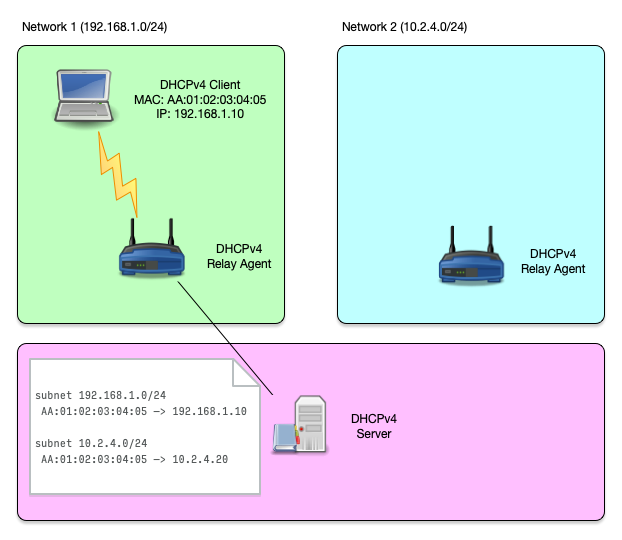
Host reservation (3/3)
Shared Subnet
Shared Subnet (1/8)
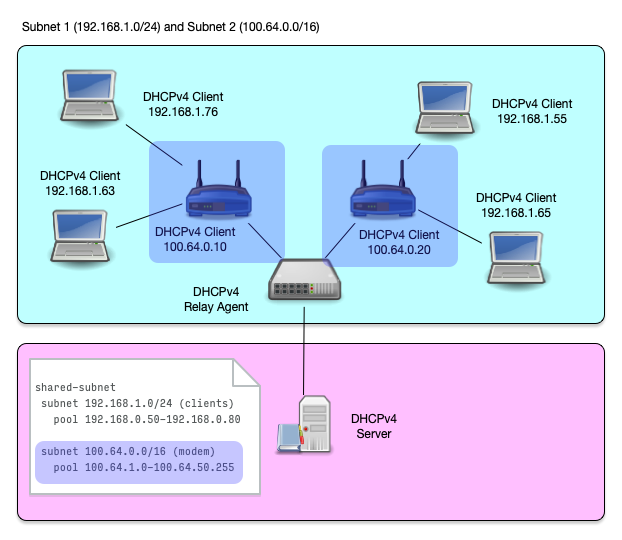
- A shared subnet is a physical network with more than one DHCPv4 managed subnet inside
- Shared subnet are sometimes created if a larger number of IP addresses are needed in a network, but because of IPv4 address shortage no contiguous range of IPv4 addresses are available
Shared Subnet (2/8)
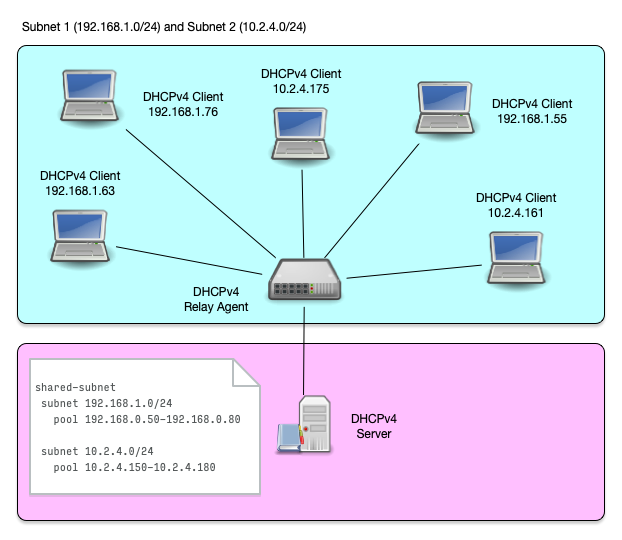
Shared Subnet (3/8)
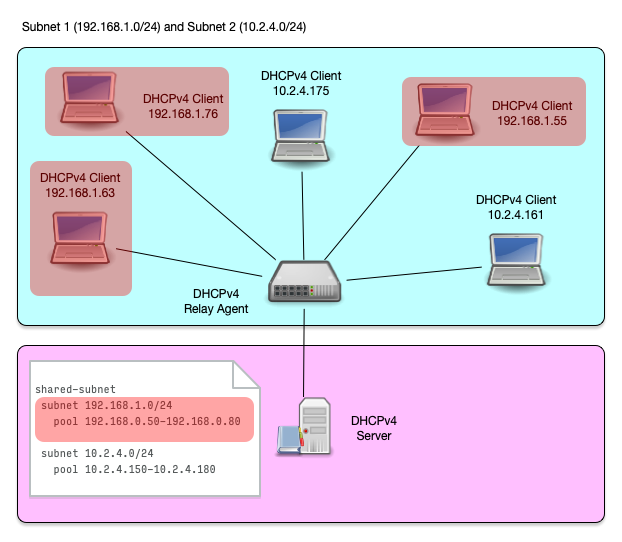
Shared Subnet (4/8)
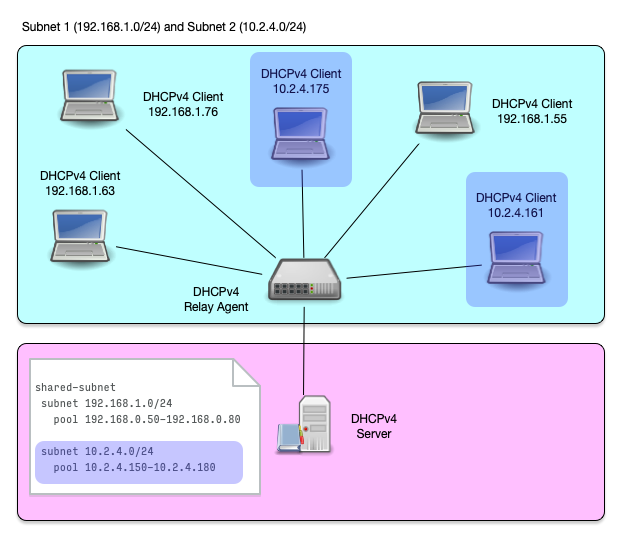
Shared Subnet (5/8)
- Another use case of shared subnets is a network where addresses
from different IPv4 subnets (and possibly different network
configuration) should be given to different network devices
- Cable modems and end user devices
- Printer, desktop and mobile devices
- POS terminals and retail infrastructure devices (digital price tags)
Shared Subnet (6/8)
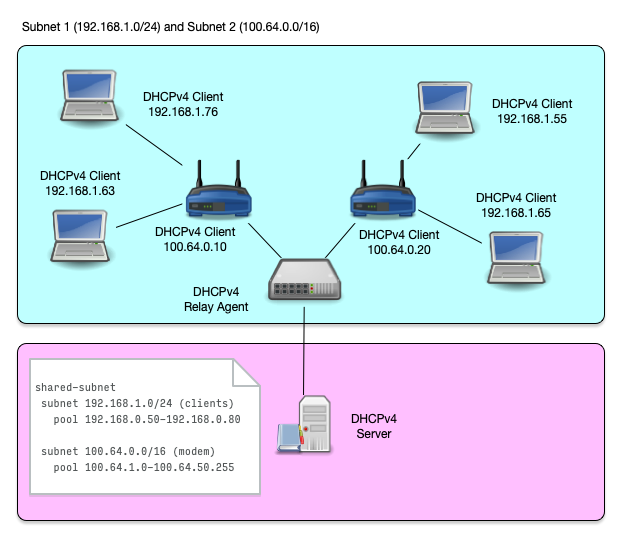
Shared Subnet (7/8)
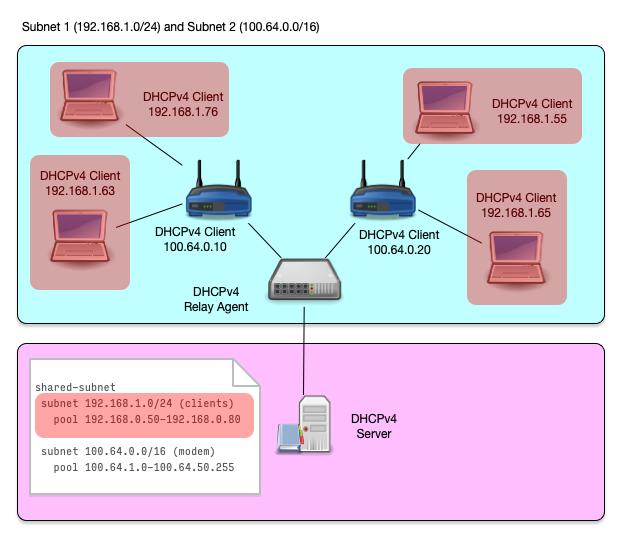
Shared Subnet (8/8)
References: RFCs, Books, recommended Webpages
Internet Standards
- DHCPv4
- RFC 2131 - DHCPv4 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- RFC 2132 - DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions
- RFC 3396 - Encoding Long Options in the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv4)
- RFC 4361 - Node-specific Client Identifiers for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Version Four (DHCPv4)
- RFC 6842 - Client Identifier Option in DHCP Server Replies
- DHCPv6
Books
- The DHCP Handbook - Understanding, Deploying, and Managing Automated Configuration Services (Ralph Droms, Ted Lemon) 1999
- IP Address Management - Principles and Practice (Timothy Rooney) 2011
- The TCP/IP Guide - A Comprehensive, Illustrated Internet Protocols Reference (Charles M. Kozierok) 2005
- Windows Server 2019 Inside Out (Orin Thomas)
Websites
- ISC Kea Documentation - https://kea.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
- ISC Knowledgebase - https://kb.isc.org/
- The TCP Guide - http://www.tcpipguide.com/
- Microsoft - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/networking/technologies/dhcp/dhcp-top