ISC Kea DHCP Training Notes
1 Agenda
- Kea DHCP Intro
- Hands-On: Preparing the Lab-Environment
- Kea Installation and Configuration
- Hands-On: Basic Kea DHCP Configuration
- Hands-On: DHCP Relay Agent
- Hands-On: Multiple Subnet Definitions
- Kea Lease Allocation
- Hands-On: DHCP Reservations
- Kea Database support
- Hands-On: Kea Database with PostgreSQL
- DNS DHCP Interactions
- Hands-On: Dynamic DNS Updates from Kea DHCP
- Kea High Availability
- Hands-On: Kea DHCP Failover Cluster
2 PDF Slides
3 Hands-On Labs
3.1 Typographic conventions in this notes
[host]$indicates a shell of an un-privileged user[host]%indicates a shell of the root user (the normal bourne shell prompt forrootis#, but that can be confused with comments in configuration files)[host]%commands for the container host[kea-server]%commands for the Kea DHCP Server machine[relay]%commands for the DHCP relay machine[bind]%commands for the DNS Server machine[clientA]%commands for the 1st DHCP client machine[clientB]%commands for the 2nd DHCP client machine
3.2 tmux - terminal multiplexer
- we will work with multiple machines (kea-server, clientA, clientB,
relay, bind9) in the lab exercises. You can open one terminal
session (SSH Session) per machine, but you can also use the
Terminal Multiplexer
tmuxwithin one terminal session - start
tmuxby executing the commandtmux - attach to a already running tmux session:
[host]% tmux attach - Help : CTRL+B - ?
- start a new tmux window : CTRL+B - c
- cancel the current window : CTRL+B - x
- next window : CTRL+B - n
- previous window : CTRL+B - p
- jump to a window : CTRL+B - <n> (0-9)
- Split-Screen (horizontal) : CTRL+B - "
- Split-Screen (vertical) : CTRL+B - %
- switch pane in split screen : CTRL+B - o
- switch pane in split screen : CTRL+B - Cursor-Arrow-Key
- tmux detach session : CTRL+B - d
4 Tools for working with JSON data (e.g. Kea DHCP config files)
4.1 JSON Editors
- JSON Hero https://jsonhero.io
- JSON Online Editor https://jsoneditoronline.org/
- JSON Viewer http://jsonviewer.stack.hu/
- JSON Lite - Firefox Browser Plugin https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/json-lite/?src=search
- Monaco Editor https://microsoft.github.io/monaco-editor/index.html
4.2 VIM JSON Syntax Highlighting
- In
vim, you can turn on syntax highlighting for JSON in the command mode with: set syntax=json - Set JSON highlighting when starting
vim% alias vimj='vim -c "set syntax=json"'
4.3 EMACS JSON Mode
- https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/JSON
- Enable JSON-Mode in Emacs with
ESC-X json-mode<enter> - Re-format a JSON file with
CTRL+c-CTRL+f
5 Kea DHCP Labs
5.1 LAB01 - ISC-KEA-DHCP Basic configuration
5.1.1 Lab network
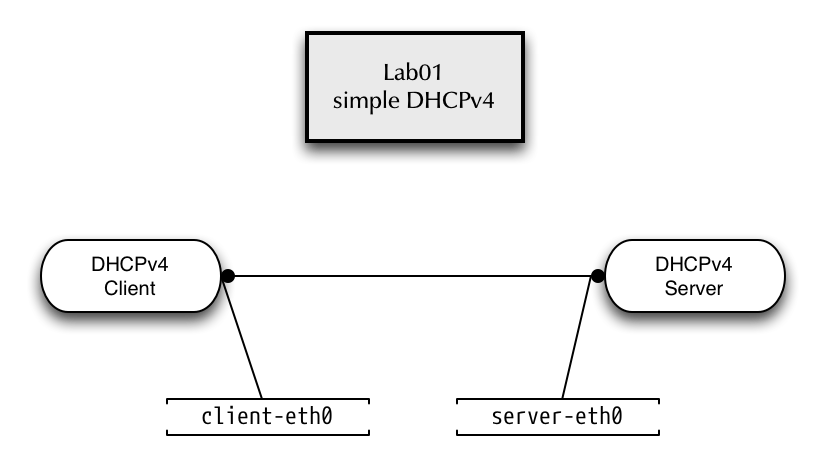
5.1.2 Prepare the Lab environment for Lab01
- Start a root-shell
[host]$ sudo -i
- Change to
/root/lab/lab01[host]% cd /root/lab/lab01
- Start the
./runshell script to start the containersclientandkea-server. Some error messages are expected when running this script (the script first tries to clean up running container that are not started at this point) - Check the running container with the command
running[host]% running kea-server client
5.2 Kea DHCPv4 Server
5.2.1 A simple DHCPv4 Server configuration
- Enter the KEA-Server container
[host]% enter kea-server
- Create the Kea DHCP Server configuration file
/etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf
{
"Dhcp4": {
"interfaces-config": {
"interfaces": [ "server-eth0" ],
"dhcp-socket-type": "raw"
},
"control-socket": {
"socket-type": "unix",
"socket-name": "kea-dhcp4.socket"
},
"lease-database": {
"type": "memfile",
"lfc-interval": 3600
},
"renew-timer": 900,
"rebind-timer": 1800,
"valid-lifetime": 3600,
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/24",
"id": 1000,
"pools": [ { "pool": "192.0.2.100 - 192.0.2.200" } ],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
}
]
}
]},
"loggers": [
{
"name": "kea-dhcp4",
"output_options": [
{
"output": "/var/log/kea/kea-dhcp4.log"
}
],
"severity": "INFO",
"debuglevel": 0
}
]
}
}
- Check the syntax of the Kea DHCP4 configuration file. This time, the Kea-DHCP4 syntax check should return with an error
% kea-dhcp4 -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf Syntax check failed with: /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf:29.7: syntax error, unexpected ",", expecting }
- Try to fix the error and check again. Solution: ( The "]}," before "loggers" has one extra "}", needs to be replaced with "]," )
- Successful Syntax check
% kea-dhcp4 -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf 2025-11-09 10:11:31.354 WARN [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/266.140058794265920] DHCPSRV_MT_DISABLED_QUEUE_CONTROL disabling dhcp queue control when multi-threading is enabled. 2025-11-09 10:11:31.354 WARN [kea-dhcp4.dhcp4/266.140058794265920] DHCP4_RESERVATIONS_LOOKUP_FIRST_ENABLED Multi-threading is enabled and host reservations lookup is always performed first. 2025-11-09 10:11:31.354 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/266.140058794265920] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_NEW_SUBNET4 a new subnet has been added to configuration: 192.0.2.0/24 with params: t1=900, t2=1800, valid-lifetime=3600 2025-11-09 10:11:31.355 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/266.140058794265920] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_SOCKET_TYPE_SELECT using socket type raw 2025-11-09 10:11:31.356 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/266.140058794265920] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_SOCKET_TYPE_SELECT using socket type raw 2025-11-09 10:11:31.357 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/266.140058794265920] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_ADD_IFACE listening on interface server-eth0 2025-11-09 10:11:31.357 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/266.140058794265920] DHCPSRV_LEASE_MGR_BACKENDS_REGISTERED the following lease backend types are available: memfile 2025-11-09 10:11:31.357 INFO [kea-dhcp4.hosts/266.140058794265920] HOSTS_BACKENDS_REGISTERED the following host backend types are available: 2025-11-09 10:11:31.357 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/266.140058794265920] DHCPSRV_FORENSIC_BACKENDS_REGISTERED the following forensic backend types are available: 2025-11-09 10:11:31.357 INFO [kea-dhcp4.database/266.140058794265920] CONFIG_BACKENDS_REGISTERED the following config backend types are available:
- Start the KEA DHCPv4 server module via systemd
% systemctl start kea-dhcp4
- Check the status of the service
% systemctl status kea-dhcp4
_ kea-dhcp4.service - Kea DHCPv4 Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kea-dhcp4.service; disabled; preset: disabled)
Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d
└─10-timeout-abort.conf
Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-11-09 10:14:56 UTC; 5min ago
Invocation: 00b9c22b660846a09d8d4ce61834680f
Docs: man:kea-dhcp4(8)
Main PID: 380 (kea-dhcp4)
Status: "Dispatching packets..."
Tasks: 6 (limit: 307)
Memory: 2.7M (peak: 2.8M)
CPU: 51ms
CGroup: /system.slice/kea-dhcp4.service
└─380 /usr/sbin/kea-dhcp4 -c /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf
Nov 09 10:14:56 34adb92738a8 systemd[1]: Starting kea-dhcp4.service - Kea DHCPv4 Server...
Nov 09 10:14:56 34adb92738a8 (ea-dhcp4)[380]: kea-dhcp4.service: ConfigurationDirectory 'kea' already exists but the mode is different. (File system: 755 ConfigurationDirectoryMode: 750)
Nov 09 10:14:56 34adb92738a8 kea-dhcp4[380]: 2025-11-09 10:14:56.153 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcp4/380.139746625256768] DHCP4_STARTING Kea DHCPv4 server version 3.0.2 (stable) starting
Nov 09 10:14:56 34adb92738a8 kea-dhcp4[380]: 2025-11-09 10:14:56.154 INFO [kea-dhcp4.commands/380.139746625256768] COMMAND_RECEIVED Received command 'config-set'
Nov 09 10:14:56 34adb92738a8 systemd[1]: Started kea-dhcp4.service - Kea DHCPv4 Server.
5.2.2 DHCP Client
- On a different Terminal (TMUX pane, separate SSH connection, new browser tab)
- Enter the client container
% enter client
- Interface
client-eth0should have no IP configuration
# ip addr show
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
10: client-eth0@if9: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether fa:34:f8:0e:a4:ff brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 1
inet6 fe80::f834:f8ff:fe0e:a4ff/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- Manually start the ISC DHCP client
[client]% dhclient -v client-eth0 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.2b1 Copyright 2004-2019 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client-eth0/72:28:b2:66:0d:f5 Sending on LPF/client-eth0/72:28:b2:66:0d:f5 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 3 (xid=0xb1f0b267) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.100 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.100 on client-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0xb1f0b267) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.100 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0xb1f0b267) bound to 192.0.2.100 -- renewal in 847 seconds.
- Kea-DHCP DHCPv4 Lease-file on the server side
[kea-server]% cat /var/lib/kea/kea-leases4.csv address,hwaddr,client_id,valid_lifetime,expire,subnet_id,fqdn_fwd,fqdn_rev,hostname,state 192.0.2.100,9e:81:8f:31:62:85,ff:8f:31:62:85:00:04:22:6c:05:90:05:96:45:33:8d:ab:47:f1:1b:bf:66:0a,3600,1544097000,1,0,0,,0
5.3 Using the DHCP-Client Script as a debugging tool
- The ISC DHCP Client executes a shell script (or binary programm)
to configure the operating system with the DHCP lease
information. While the
dhclientbinary is the same of different operating systems (Linux, BSD, commercial Unix), the shell script takes over the system dependent part - The lease parameters are given to the script in form of environment
variables that can be printed out with the
envshell command - Stop a previous running
dhclientprocess[client]% dhclient -r
- Start the
dhclientprogram using the script and inspect the output.[client]% dhclient -v -sf /usr/bin/env client-eth0
5.4 Kea-DHCP-Server REST API and dynamic reconfiguration
5.4.1 Configuring the Kea Control Agent
- A Kea-DHCP server takes control commands over a
unixsocket. The socket location is defined in the Kea-Server configuration file. Make sure the socket definition for the DHCPv4 server looks like this
{
"Dhcp4": {
"control-socket": {
"socket-type": "unix",
"socket-name": "kea-dhcp4.socket"
},
"lease-database": {
[...]
- Test the configuration and restart the service
[kea-server]% kea-dhcp4 -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf [kea-server]% systemctl restart kea-dhcp4
- On the Kea-Server machine, create a configuration for the Kea
Control Agent in the file
/etc/kea/kea-ctrl-agent.conf, listening on an HTTP-REST API Endpoint port 9099 on IPv6localhost:
{
"Control-agent": {
"http-host": "::1",
"http-port": 9099,
"control-sockets": {
"dhcp4": {
"socket-type": "unix",
"socket-name": "kea-dhcp4.socket"
}
},
"loggers": [
{
"name": "kea-ctrl-agent",
"severity": "INFO",
"output_options": [
{
"output": "/var/log/kea/kea-ctrl-agent.log"
}
]
}
]
}
}
- Check the configuration file for syntax errors
[kea-server]% kea-ctrl-agent -t /etc/kea/kea-ctrl-agent.conf
- Test the control agent configuration and start the agent:
[kea-server]% systemctl start kea-ctrl-agent
[kea-server]% systemctl status kea-ctrl-agent
● kea-ctrl-agent.service - Kea Control Agent
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kea-ctrl-agent.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-09-24 19:27:21 UTC; 6s ago
Docs: man:kea-ctrl-agent(8)
Main PID: 117 (kea-ctrl-agent)
Tasks: 5 (limit: 307)
Memory: 1.5M
CPU: 13ms
CGroup: /system.slice/kea-ctrl-agent.service
└─ 117 /usr/sbin/kea-ctrl-agent -c /etc/kea/kea-ctrl-agent.conf
Sep 24 19:27:21 f5d068ba20fb systemd[1]: Started kea-ctrl-agent.service - Kea Control Agent.
Sep 24 19:27:21 f5d068ba20fb kea-ctrl-agent[117]: 2022-09-24 19:27:21.771 INFO [kea-ctrl-agent.dctl/117.139862882936704] DCTL_STARTING Control-agent starting, pid: 117, version:>
- Sending API calls via
curl. Here we send theconfig-getcommand to the DHCPv4 server
[kea-server]% curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "command": "config-get", "service": [ "dhcp4" ] }' \
http://[::1]:9099/
- The output is unformatted JSON. The tool
jqcan be used to pretty-print the output
[kea-server]% curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "command": "config-get", "service": [ "dhcp4" ] }' \
http://[::1]:9099/ | jq
jqcan be used to filter specific parts of the configuration. Thejqfilter".[ 0 ].arguments"can be used to produce a valid Kea configuration file:
[kea-server]% curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "command": "config-get", "service": [ "dhcp4" ] }' \
http://[::1]:9099/ | jq ".[0].arguments.Dhcp4.loggers"
[
{
"debuglevel": 0,
"name": "kea-dhcp4",
"output_options": [
{
"flush": true,
"maxsize": 10240000,
"maxver": 1,
"output": "/var/log/kea-dhcp4.log",
"pattern": ""
}
],
"severity": "INFO"
}
]
- The
list-commandscommand returns back the API commands available for a specific Kea module
[kea-server]% curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "command": "list-commands", "service": [ "dhcp4" ] }' \
http://[::1]:9099/ | jq
5.4.2 Dynamic changes to the Kea configuration file
- Dump the current configuration into the file
kea-dhcp4.tmp
[kea-server]% curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "command": "config-get", "service": [ "dhcp4" ] }' \
http://[::1]:9099/ | jq ".[0]" > kea-dhcp4.tmp
- Edit the file, add the
commandandserviceinformation, remove theresultand thehashstructure at the end of the file and make changes to the configuration (in this example we set the DHCP server to be authoritative):
{
"command": "config-set",
"service": [ "dhcp4" ],
"arguments": {
"Dhcp4": {
"authoritative": true,
"boot-file-name": "",
"calculate-tee-times": false,
[...]
- Send the new configuration to the server
[kea-server]% curl -s -X POST \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d @kea-dhcp4.tmp http://[::1]:9099/ | jq
- Successful result
[
{
"arguments": {
"hash": "D6D7402E4852BE6278F4122781D6C80F3F0DE5B3C77AEC23891E860EF0C7D677"
},
"result": 0,
"text": "Configuration successful."
}
]
- All dynamic changes are stored in memory. In order to make the changes persistent, write the in-memory configuration back to a file (be careful, any comments in the file will be gone and the formatting will be different)
- Writing the new file via the API fails. Why? What do we need to change to make the
config-writeAPI command work?- Solution: The directory
/etc/keamust be owned by thekeauser:chown kea: /etc/kea
- Solution: The directory
[kea-server]% curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{ "command": "config-write", "arguments": { "filename": "/etc/kea/kea-dhcp4-new.json" }, "service": [ "dhcp4" ] }' \
http://[::1]:9099/ | jq
- Successful result
[
{
"arguments": {
"filename": "/etc/kea/kea-dhcp4-new.json",
"size": 3248
},
"result": 0,
"text": "Configuration written to /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4-new.json successful"
}
]
5.4.3 Closing the lab01 setup
- Exit both the Kea-Server container and the client container
- Execute both the
./stopand the./cleanscripts on the host (inside directory/root/lab/lab01)
5.5 LAB02 - ISC-DHCP Relay-Agent
5.5.1 Lab network
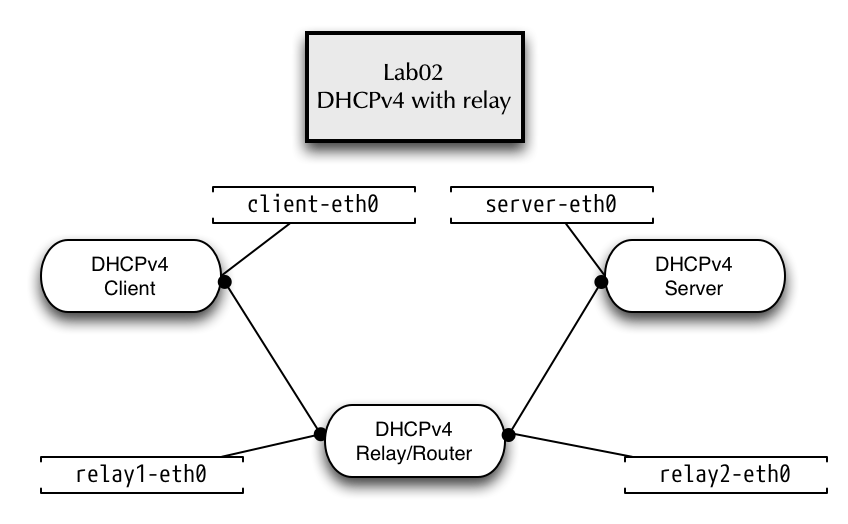
5.5.2 DHCPv4 with relay agent
- We work in directory
lab02and start the lab container
[host]% cd /root/lab/lab02 [host]% ./run
- We will start the DHCPv4 relay agent on the container named "relay"
[host]% enter relay
- The relay agent will listen on interface
relay1-eth0for DHCP broadcast messages and will forward these messages to the Kea-DHCP-Server on address 100.64.0.1
[relay]% dhcrelay -id relay1-eth0 -iu relay2-eth0 -d 100.64.0.1 Requesting: relay1-eth0 as upstream: N downstream: Y Requesting: relay2-eth0 as upstream: Y downstream: N Dropped all unnecessary capabilities. Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Relay Agent 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/relay2-eth0/86:4e:49:be:7f:f5 Sending on LPF/relay2-eth0/86:4e:49:be:7f:f5 Listening on LPF/relay1-eth0/26:db:ff:96:95:92 Sending on LPF/relay1-eth0/26:db:ff:96:95:92 Sending on Socket/fallback Dropped all capabilities.
- On a different terminal (tmux pane or window), we enter the Kea DHCP server container
[host]% enter kea-server
- As the DHCP requests from clients will now be received by the
Kea-Server via UDP unicast, we can configure Kea to listen on UDP
socket only:
"dhcp-socket-type": "udp" - Edit the file
/etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf:
{
"Dhcp4": {
"interfaces-config": {
"interfaces": [ "server-eth0" ],
"dhcp-socket-type": "udp"
},
[...]
- Test the Kea DHCP4 configuration file
[kea-server]% kea-dhcp4 -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf
- Start the Kea-Server and make sure it is running
[kea-server]% systemctl start kea-dhcp4
[kea-server]% systemctl status kea-dhcp4
● kea-dhcp4.service - Kea DHCPv4 Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kea-dhcp4.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-09-24 19:37:28 UTC; 6s ago
Docs: man:kea-dhcp4(8)
Main PID: 73 (kea-dhcp4)
Tasks: 5 (limit: 307)
Memory: 2.2M
CPU: 27ms
CGroup: /system.slice/kea-dhcp4.service
└─ 73 /usr/sbin/kea-dhcp4 -c /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf
Sep 24 19:37:28 ee321a75def3 systemd[1]: Started kea-dhcp4.service - Kea DHCPv4 Server.
Sep 24 19:37:28 ee321a75def3 kea-dhcp4[73]: 2022-09-24 19:37:28.613 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcp4/73.139839369592128] DHCP4_STARTING Kea DHCPv4 server version 2.2.0 (stable) starting
- Next, on a third terminal (tmux pane or window), enter the
clientcontainer
[host]% enter client
- Start the
dhclientprogram to request a DHCP lease
[client]% dhclient -v client-eth0 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium.All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client-eth0/7a:7e:17:40:ca:a7 Sending on LPF/client-eth0/7a:7e:17:40:ca:a7 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 6 (xid=0xec227646) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.100 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.100 on client-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0xec227646) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.100 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0xec227646) bound to 192.0.2.100 -- renewal in 760 seconds.
- Output on the relay terminal screen
Forwarded BOOTREQUEST for 7a:7e:17:40:ca:a7 to 100.64.0.1 BOOTREPLY giaddr: 192.0.2.1 Forwarded BOOTREPLY for 7a:7e:17:40:ca:a7 to 192.0.2.100 Forwarded BOOTREQUEST for 7a:7e:17:40:ca:a7 to 100.64.0.1 BOOTREPLY giaddr: 192.0.2.1 Forwarded BOOTREPLY for 7a:7e:17:40:ca:a7 to 192.0.2.100
5.5.3 Inspecting DHCP traffic with tcpdump
- On the Kea-Server container, make the DHCP communication between
the relay-agent and the DHCP-Server visible using
tcpdump.[kea-server]% tcpdump -vv -i server-eth0 port 67 or port 68
- Start a new client lease request from the client (
dhclient -rreleases the lease and stops thedhclientbackground process).[client]% dhclient -r [client]% dhclient -v -sf /usr/bin/env client-eth0
5.5.4 Lab 02 Cleanup
- Exit the
client,relayandkea-servermachines - Execute the scripts
./stopand./cleanin/root/kea/lab02/on the host
5.6 LAB03 - Multiple subnet definitions
5.6.1 Lab network
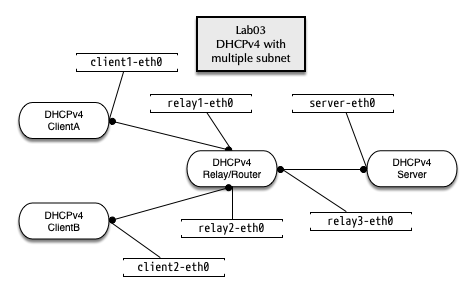
- Change into the directory
/root/lab/lab03on the VM host - Execute the
./runscript
5.6.2 Defining two subnet with pools
- Enter the
kea-servercontainer% enter kea-server
- Add a new subnet for 198.100.51.0/24 to the Kea DHCP4 configuration
[...]
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/24",
"id": 1000,
"pools": [ { "pool": "192.0.2.100 - 192.0.2.200" } ],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
}
]
},
{
"subnet": "198.100.51.0/24",
"id": 2000,
"pools": [ { "pool": "198.100.51.50 - 198.100.51.90" } ],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "198.100.51.1"
}
]
}
[...]
- Test the configuration file:
[kea-server]% kea-dhcp4 -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf 2022-09-24 19:50:11.610 INFO [kea-dhcp4.hosts/70.140044011437376] HOSTS_BACKENDS_REGISTERED the following host backend types are available: mysql postgresql 2022-09-24 19:50:11.611 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/70.140044011437376] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_SOCKET_TYPE_SELECT using socket type udp 2022-09-24 19:50:11.612 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/70.140044011437376] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_ADD_IFACE listening on interface server-eth0 2022-09-24 19:50:11.613 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/70.140044011437376] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_NEW_SUBNET4 a new subnet has been added to configuration: 192.0.2.0/24 with params: t1=900, t2=1800, valid-lifetime=3600 2022-09-24 19:50:11.614 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcpsrv/70.140044011437376] DHCPSRV_CFGMGR_NEW_SUBNET4 a new subnet has been added to configuration: 198.100.51.0/24 with params: t1=900, t2=1800, valid-lifetime=3600
- Start the Kea DHCPv4 server and make sure it is running
[kea-server]% systemctl start kea-dhcp4
[kea-server]% systemctl status kea-dhcp4
● kea-dhcp4.service - Kea DHCPv4 Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kea-dhcp4.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-09-24 19:50:50 UTC; 5s ago
Docs: man:kea-dhcp4(8)
Main PID: 77 (kea-dhcp4)
Tasks: 5 (limit: 307)
Memory: 2.4M
CPU: 23ms
CGroup: /system.slice/kea-dhcp4.service
└─ 77 /usr/sbin/kea-dhcp4 -c /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf
Sep 24 19:50:50 31f3bf1e39a3 systemd[1]: Started kea-dhcp4.service - Kea DHCPv4 Server.
Sep 24 19:50:50 31f3bf1e39a3 kea-dhcp4[77]: 2022-09-24 19:50:50.327 INFO [kea-dhcp4.dhcp4/77.140333779688768] DHCP4_STARTING Kea DHCPv4 server version 2.2.0 (stable) starting
- On a new terminal, enter the relay container and start the ISC DHCP
relay agent
% enter relay
- Start the ISC DHCP relay-agent
[relay]% dhcrelay -id relay1-eth0 -id relay2-eth0 -iu relay3-eth0 -d 100.64.0.1 Requesting: relay1-eth0 as upstream: N downstream: Y Requesting: relay2-eth0 as upstream: N downstream: Y Requesting: relay3-eth0 as upstream: Y downstream: N Dropped all unnecessary capabilities. Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Relay Agent 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/relay3-eth0/82:e3:ae:60:fe:2d Sending on LPF/relay3-eth0/82:e3:ae:60:fe:2d Listening on LPF/relay2-eth0/1e:00:4b:c8:6a:5d Sending on LPF/relay2-eth0/1e:00:4b:c8:6a:5d Listening on LPF/relay1-eth0/56:8f:f7:82:a3:be Sending on LPF/relay1-eth0/56:8f:f7:82:a3:be Sending on Socket/fallback Dropped all capabilities.
- Test the DHCP Client from container
clientAandclientB(each in it's own Terminal or TMUX session)
[host]% enter clientA [clientA]% dhclient -v client1-eth0 [host]% enter clientB [clientB]% dhclient -v client2-eth0
5.6.3 Find and fix the issue with clientB
- ClientA will succeed to get an IP-Address, but ClientB will fail. Why?
- Check the logfile on the Kea-Server in
/var/log/kea/kea-dhcp4.log - Compare the IP-Addresses used on the relay with the IP addresses used in the subnet configuration on the Kea server
5.6.4 Solution: there was a number switch typo in the configuration
- Correct subnet configuration (198.51.100.0/24 instead of 198.100.51.0/24):
[...]
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/24",
"pools": [ { "pool": "192.0.2.100 - 192.0.2.200" } ],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
}
]
},
{
"subnet": "198.51.100.0/24",
"pools": [ { "pool": "198.51.100.50 - 198.51.100.90" } ],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "198.51.100.1"
}
]
}
[...]
- Re-test the configuration and restart the server, test from
clientB
5.6.5 Adding global DHCP options
- Now we want to send additional DHCP option to the client machines. We start with the list of DNS resolvers and (next exercise) the local domain name. As the DNS resolver are the same for each subnet, we define the DHCP options on the global server level:
"Dhcp4": {
"option-data": [
{
"name": "domain-name-servers",
"code": 6,
"space": "dhcp4",
"csv-format": true,
"data": "100.64.53.53"
}
],
[...]
- Test from
clientAandclientB
[clientB]% dhclient -r Killed old client process [clientB]% dhclient -v client2-eth0 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 8 (xid=0x6ba76b02) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.100 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.100 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x6ba76b02) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.100 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x6ba76b02) bound to 192.0.2.100 -- renewal in 820 seconds.
- Check that the DNS resolver has been written to
/etc/resolv.conf
[clientB]% cat /etc/resolv.conf ; generated by /usr/sbin/dhclient-script nameserver 100.64.53.53
5.6.6 Adding a subnet specific DHCP option
- The client container machines are in different DNS domains.
clientAis in the Domaina.example.com, whileclientBis in the Domainb.example.com. - We define a subnet specific DHCP option for each subnet in file
/etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf. Add thedomain-nameoption with a different value into each of the two subnet definitions:
[...]
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/24",
"pools": [ { "pool": "192.0.2.100 - 192.0.2.200" } ],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
},
{
"name": "domain-name",
"data": "a.example.com"
}
]
},
[...]
- Test the configuration file, restart the Kea DHCP server and check that the server is running without error messages.
- Test the new DHCP option from the DHCP clients, make sure that the
different DNS domains appear in the
searchclause in the file/etc/resolv.conf
[clientA]% dhclient -r Killed old client process [clientA]% dhclient -v client1-eth0 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/a2:63:58:fb:24:eb Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/a2:63:58:fb:24:eb Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client2-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 5 (xid=0x8b907733) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.150 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.150 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x8b907733) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.150 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x8b907733) bound to 192.0.2.150 -- renewal in 729 seconds.
- Inspect the clients resolver configuration
[clientA]% cat /etc/resolv.conf ; generated by /usr/sbin/dhclient-script search a.example.com nameserver 100.64.53.53
5.7 User Context as Comments
- Shell, C, or C++ style comments are all permitted in the "extended"
JSON flavor used by the Kea configuration files. However these
non-standard extension of JSON do not work with externel JSON tools
(JSON highlighting in editors, tools like
jqoryq) and are lost after loading into Kea. - Kea also supports "user-context" JSON objects inside global,
shared-network, subnet, pool, host reservation, option, option
definition, client-class, control-socket, dhcp-ddns, interfaces,
loggers (and for DHCPv6 pd-pool and server-id) level. A
user-contextJSON structure will not be evaluated by Kea, but will be retained in the configuration when using theconfig-getandconfig-setAPI calls: https://kea.readthedocs.io/en/latest/arm/config.html#comments-and-user-context - Example:
{
"command": "config-set",
"service": [ "dhcp4" ],
"arguments": {
"Dhcp4": {
"user-context": {
"comment": "This is a comment in the user context",
"comment02": "/user-context/ Blocks can contain any JSON structures",
"comment03": "The user context blocks are loaded by the Kea parser but ignored by the Kea server",
"ResponsibleAdmin": "Joe Doe",
"Location": "Datacenter NY"
},
"authoritative": false,
"boot-file-name": "",
"calculate-tee-times": false,
5.8 DHCP reservations
5.8.1 Creating a DHCP reservation
- Kea DHCP supports reservations of client leases based on hardware
interface addresses (MAC-Address), DHCP Unique ID (DUID),
Relay-Circut-ID or Client-ID. Lookup the Hardware-MAC-Address of
your
clientAmachine with the commandip link showand create a reservation based on that hardware address:
[...]
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/24",
"pools": [
{
"pool": "192.0.2.100 - 192.0.2.200"
}
],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
},
{
"name": "domain-name",
"data": "a.example.com"
}
],
"reservations": [
{
"hw-address": "xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx",
"ip-address": "192.0.2.210",
"hostname": "client.a"
}
]
},
[...]
- Test the configuration and restart the Kea DHCPv4 server
- Check from
clientAthat the reserved IPv4 address is assigned and the hostname is delivered
[clientA]% dhclient -r Killed old client process [ClientA]% dhclient -v -sf /usr/bin/env client1-eth0 | grep host_name Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 7 (xid=0x4718c87c) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.210 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.210 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x4718c87c) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.210 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x4718c87c) new_host_name=client.a requested_host_name=1 bound to 192.0.2.210 -- renewal in 693 seconds.
5.9 Shared-Network
5.9.1 Create a shared network configuration
- A shared network is a physical subnet with multiple IP networks.
- One shared network definition can contain two or more subnet definitions
- Options can be defined on the shared-network, subnet and pool level
[...]
"shared-networks": [
{
"name": "kea-lab01",
"relay": {
"ip-addresses": [ "192.0.2.1" ]
},
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/26",
"id": 1000,
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
}
],
"pools": [
{
"pool": "192.0.2.60 - 192.0.2.61"
}
]
},
{
"subnet": "10.0.0.0/24",
"id": 2000,
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "10.0.0.1"
}
],
"pools": [
{
"pool": "10.0.0.10 - 10.0.0.11"
}
]
}
]
}
],
[...]
- Replace the subnet4 definition in the Kea-DHCP4 Server configuration with the shared-network configuration above. Test the new configuration and restart the Kea server
[kea-server]% kea-dhcp4 -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf [kea-server]% systemctl restart kea-dhcp4
- To test the shared network, we request multiple IP adresses with
different client-identifier (the
-C client-idswitch with thedhclienttool) until we see an IP address on the client from both subnet pools defined inside the shared network defintion - Without client classification, Kea might choose an IP address for any pool from all subnets inside the shared network
- Remove the client configuration file
/etc/dhcp/dhclient.conf(created in the previous lab about custom DHCP option)
[clientA]% pkill dhclient [clientA]% rm -f /var/lib/dhclient/dhclient.leases [clientA]% dhclient -v -C test01 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 5 (xid=0x6f6a8f66) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.60 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.60 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x6f6a8f66) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.60 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x6f6a8f66) bound to 192.0.2.60 -- renewal in 781 seconds. [clientA]% pkill dhclient [clientA]% rm -f /var/lib/dhclient/dhclient.leases [clientA]% dhclient -v -C test04 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 8 (xid=0x9434fe39) DHCPOFFER of 10.0.0.10 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 10.0.0.10 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x9434fe39) DHCPACK of 10.0.0.10 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x9434fe39) bound to 10.0.0.10 -- renewal in 882 seconds.
5.10 Adjust lease times (and other fields)
- DHCP configuration options can be adjusted on global, subnet, pool, and shared-subnet scope. In this exercise we will change the lease times on a subnet:
[...]
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/24",
"renew-timer": 90,
"rebind-timer": 180,
"valid-lifetime": 360,
"pools": [
{
"pool": "192.0.2.100 - 192.0.2.200"
}
],
[...]
- Test the new lease times on
clientA(should now be < 90 seconds):
[clientA]% dhclient -r Killed old client process [ClientA]% rm -f /var/lib/dhclient/dhclient.leases [ClientA]% dhclient -v Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/ae:09:28:70:9b:e5 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 6 (xid=0x15689123) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.60 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.60 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x15689123) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.60 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x15689123) bound to 192.0.2.60 -- renewal in 85 seconds.
5.11 Client-Classing and Vendor-Options
5.11.1 Automatic vendor classing
- Selecting subnet based on the vendor option (Option 60). The vendor options used in this exercise are examples and not the real-world vendor option values:
"shared-networks": [
{
"name": "kea-lab01",
"relay": {
"ip-addresses": [ "192.0.2.1" ]
},
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/26",
"id": 1000,
"client-classes": [ "VENDOR_CLASS_windows13" ], # <-- Windows 13 Clients will get IP
# from this subnet
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
}
],
"pools": [
{
"pool": "192.0.2.60 - 192.0.2.63"
}
]
},
{
"subnet": "10.0.0.0/24",
"id": 2000,
"client-classes": [ "VENDOR_CLASS_fedoraLinux" ], # <-- Fedora-Linux Clients will get IP
# from this subnet
"option-data": [
[...]
- Test the configuration and restart the Kea DHCP4 server
- Requesting a lease with vendor option
fedoraLinux
[clientA]% dhclient -r Killed old client process [clientA]% dhclient -v -V fedoraLinux Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/62:76:c3:d1:32:03 Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/62:76:c3:d1:32:03 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 6 (xid=0x8a7c4452) DHCPOFFER of 10.0.0.10 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 10.0.0.10 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x8a7c4452) DHCPACK of 10.0.0.10 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x8a7c4452) bound to 10.0.0.10 -- renewal in 759 seconds.
- Requesting a lease with vendor option "windows13"
[clientA]% dhclient -r Killed old client process [clientA]% dhclient -v -V windows13 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.3 Copyright 2004-2022 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/client1-eth0/62:76:c3:d1:32:03 Sending on LPF/client1-eth0/62:76:c3:d1:32:03 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 4 (xid=0x49246425) DHCPOFFER of 192.0.2.60 from 192.0.2.1 DHCPREQUEST for 192.0.2.60 on client1-eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 (xid=0x49246425) DHCPACK of 192.0.2.60 from 192.0.2.1 (xid=0x49246425) bound to 192.0.2.60 -- renewal in 74 seconds.
5.11.2 Dynamic client classing based on expressions
- Configuration for dynamic client classing based on the vendor option content
"Dhcp4": {
"client-classes": [
{
"name": "windows",
"test": "substring(option[60].hex,0,3) == 'win'",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "domain-name",
"data": "win.example.com"
}
]
},
{
"name": "other",
"test": "not(substring(option[60].hex,0,3) == 'win')",
"option-data": [
{
"name": "domain-name",
"data": "other.example.com"
}
]
}
],
[...]
"shared-networks": [
{
"name": "kea-lab01",
"relay": {
"ip-addresses": [
"192.0.2.1"
]
},
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "192.0.2.0/26",
"id": 1000,
"client-classes": [ "windows" ],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "192.0.2.1"
}
],
"pools": [
{
"pool": "192.0.2.60 - 192.0.2.63"
}
]
},
{
"subnet": "10.0.0.0/24",
"id": 2000,
"client-classes": [ "other" ],
"pools": [
{
"pool": "10.0.0.100 - 10.0.0.149"
}
],
"option-data": [
{
"name": "routers",
"data": "10.0.0.1"
}
]
}
]
}
],
[...]
- Test the configuration and restart the Kea DHCP4 Server
- Test requesting a lease from a vendor option that is not a Windows client
[clientA]% dhclient -v -V freebsd
- Test requesting a lease from a vendor option that is a Windows client
[clientA]% dhclient -v -V windows11
5.11.3 Client-Classing with regular expressions
- Starting with Kea-DHCP 3.x, client classes can match with regular expressions
- The following client class looks into the OUI-part of the hardware address and tests if they are from Apple Computers range of OUI-Adresses:
"client-classes": [
{
"name": "Apple-Computer",
"test": "match('5c-1b-f4|a8-5b-b7|58-55-95|00-19-b8',hexstring(substring(pkt4.mac, 0, 3), '-'))"
},
[...]
- Client-Classing tests run for each incoming DHCP request
- Complex regular expressions can be CPU intensive and can slow down the DHCP server
5.11.4 Debugging client classing
- Watch for the test evaluation results in the Kea DHCP4 log file
[kea-server]% tail -f /var/log/kea-dhcp4.log
- Enabling debug output in the Kea DHCP4 configuration file
"loggers": [ {
"name": "kea-dhcp4.eval",
"output_options": [ {
"output": "/var/log/kea-dhcp4-eval.log"
} ],
"severity": "DEBUG",
"debuglevel": 99
} ]
- Example output of the Kea DHCPv4 eval logging
2021-10-01 09:42:02.503 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_OPTION Pushing option 60 with value 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '0' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '3' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_SUBSTRING_EMPTY Popping length 3, start 0, string 0x pushing result 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string 'win' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_EQUAL Popping 0x77696E and 0x pushing result 'false' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_OPTION Pushing option 60 with value 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '0' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '3' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_SUBSTRING_EMPTY Popping length 3, start 0, string 0x pushing result 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string 'win' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_EQUAL Popping 0x77696E and 0x pushing result 'false' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.504 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_NOT Popping 'false' pushing 'true' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.505 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_OPTION Pushing option 60 with value 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.505 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '0' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.505 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '3' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.505 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_SUBSTRING_EMPTY Popping length 3, start 0, string 0x pushing result 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string 'win' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_EQUAL Popping 0x77696E and 0x pushing result 'false' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_OPTION Pushing option 60 with value 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '0' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string '3' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_SUBSTRING_EMPTY Popping length 3, start 0, string 0x pushing result 0x 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_STRING Pushing text string 'win' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_EQUAL Popping 0x77696E and 0x pushing result 'false' 2021-10-01 09:42:02.506 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_NOT Popping 'false' pushing 'true' 2021-10-01 09:42:05.616 DEBUG [kea-dhcp4.eval/445.140222409295296] EVAL_DEBUG_OPTION Pushing option 60 with value 0x77696E646F777337
5.11.5 Client classing in reservations
- Clients can be associated to a client-class using a reservation (using the Hardware-Address, DUID, Client-ID, Relay-ID)
[...]
"subnet4": [
{
"subnet": "10.0.0.0/24",
"pools": [ { "pool": "10.0.0.10-10.0.0.100" } ],
"reservations": [
{
"hw-address": "01:02:03:04:05:06",
"client-classes": [ "windows", "staff" ]
}
]
}
],
[...]
5.12 Kea Database with PostgreSQL
- For this lab we continue to use
lab03.[host]% enter kea-server
5.12.1 Storing Leases in Postgresql
- Enter the
kea-servercontainer - Initialize and start the PostgreSQL Database
[kea-server]% /usr/bin/postgresql-setup --initdb [kea-server]% systemctl enable --now postgresql
- Connect to the database server. This PostgreSQL-Server does not have a password set, use the empty password to log in. For a production installation, configure password authentication for the database server. PostgreSQL authentication configuration is out of scope of the ISC Kea DHCP training.
[kea-server]% su - postgres [kea-server]$ psql postgres psql (18.0) Type "help" for help. postgres=#
- Create a new database,
kea_lease_dbis the name of the database in this example
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE kea_lease_db; CREATE DATABASE
- Create a user for Kea server to access the database
postgres=# CREATE USER kea WITH PASSWORD 'secure-password'; CREATE ROLE
- Set the permissions for the new user on the database
postgres=# GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE kea_lease_db TO kea; GRANT
- In PostgreSQL 15 (and higher) you must make the user
keathe owner of the database and give this user the rights to change the database schema (see https://www.cybertec-postgresql.com/en/error-permission-denied-schema-public/)
postgres=# GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public TO kea; postgres=# ALTER DATABASE kea_lease_db OWNER TO kea;
- Leave PostgreSQL client
postgres=# \q
- Leave the shell with user
postgresto be userrootagain
[kea-server]$ exit [kea-server]% id uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
- Configure the PostgreSQL Database to use
passwordauthentication for the Kea database. The Kea database entries must appear before thealldatabase entries in the file/var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD local kea_lease_db kea password host kea_lease_db kea 127.0.0.1/32 password host kea_lease_db kea ::1/128 password # "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only local all all peer [...]
- Restart the PostgreSQL database server
[kea-server]% systemctl restart postgresql
- Create the database tables using the
kea-admintool
[kea-server]% kea-admin db-init pgsql -u kea -h 127.0.0.1 -p secure-password -n kea_lease_db
- Add support for the PostgreSQL-Database to Kea-DHCP with the database hook:
{ "Dhcp4": { "hooks-libraries": [ { "library": "/usr/lib64/kea/hooks/libdhcp_pgsql.so" } ], - Adjust the
lease-databaseblock in the Kea server configuration to use a PostgreSQL-type database:
[...]
"lease-database": {
"type": "postgresql",
"host": "localhost",
"name": "kea_lease_db",
"user": "kea",
"password": "secure-password"
},
[...]
- Test the configuration file and restart the Kea DHCP server
- Test requesting a lease from
clientA - Dump the lease database using the
kea-admintool
[kea-server]% kea-admin lease-dump pgsql -u kea -h 127.0.0.1 \
-p secure-password -n kea_lease_db -o leases.csv -4
lease4 successfully dumped to leases.csv
[kea-server]% less leases.csv
address,hwaddr,client_id,valid_lifetime,expire,subnet_id,fqdn_fwd,fqdn_rev,hostname,state
192.0.2.100,fe15e927353b,ffe927353b000400d52b989bf14fbfaeb1f21908f229d9,3600,2018-12-08 21:39:06+00,1,0,0,,default
5.12.2 Host/Reservation Database in a SQL Database
- A host database can be created the same way as the lease database (instructions above)
[...]
"host-database": {
"type": "postgresql",
"host": "localhost",
"name": "kea_host_db",
"user": "kea",
"password": "secure-password"
},
[...]
- If the database content is maintained via database updates, the host/reservation database can be configured in read-only mode:
[...]
"host-database": {
"readonly": true,
"type": "postgresql",
"host": "localhost",
"name": "kea_host_db",
"user": "kea",
"password": "secure-password"
},
[...]
5.12.3 Host Commands
- See https://kea.readthedocs.io/en/latest/arm/hooks.html#host-cmds-host-commands
- The hook application that offers a number of new commands used to query and manipulate host reservations. Kea provides a way to store host reservations in a database. In many larger deployments it is useful to be able to manage that information while the server is running. This library provides management commands for adding, querying and deleting host reservations in a safe way without restarting the server.
5.12.4 Managing Reservations through the SQL database
- The Host-Reservations can be managed directly on the SQL database layer, without the need of the host commands hook. However this is less convinient and the SQL code needs to be adapted when the SQL table schema changes between Kea release versions
- The document from ISC describes how to manage host reservations on the SQL level: https://gitlab.isc.org/isc-projects/kea/-/wikis/docs/editing-host-reservations
- It is recommended to create a wrapper around the SQL commands to use from the command line or a web interface
5.13 LAB04 - Dynamic DNS updates from Kea DHCP
5.13.1 Lab network
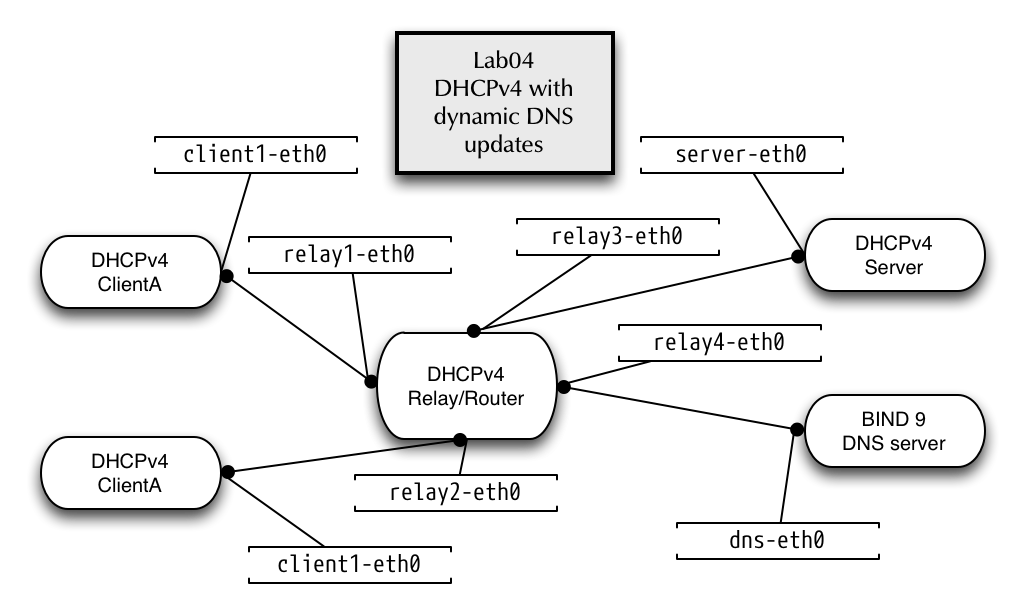
- Create the container configuration for the dynamic DNS updates lab
[host]% /root/lab/lab03/stop [host]% /root/lab/lab03/clean [host]% cd /root/lab/lab04 [host]% ./run
5.13.2 Preparing a BIND 9 DNS server
- Create a simple BIND 9 configuration
[host]% enter bind9 [bind9]% systemctl edit --full named [...] Environment=NAMEDCONF=/etc/namedb/named.conf [..] [bind9]% cd /etc/namedb [bind9]% $EDITOR named.conf
- BIND 9 configuration file
options {
recursion no;
directory "/etc/namedb";
};
zone "example.com" {
type master;
allow-update { 100.64.0.1; };
file "example.com";
};
- Create a simple zone file for the domain
example.com
[bind9]% $EDITOR example.com
- Content of the
example.comzonefile
$TTL 1h
@ IN SOA dns.example.com. hostmaster 1001 2h 30m 41d 1h
IN NS dns.example.com.
dns IN A 100.64.53.1
- Adjust the file and directory permissions
[bind9]% chown -R named /etc/namedb
- Check configuration and start the BIND 9 DNS-Server
[bind9]% named-checkconf -z /etc/namedb/named.conf
zone example.com/IN: loaded serial 1001
[bind9]% systemctl enable --now named
[bind9]% systemctl status named
● named.service - Berkeley Internet Name Domain (DNS)
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/named.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2018-12-08 21:21:31 UTC; 2s ago
Process: 114 ExecStop=/bin/sh -c /usr/sbin/rndc stop > /dev/null 2>&1 || /bin/kill -TERM $MAINPID (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 123 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/named -u named -c ${NAMEDCONF} $OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 121 ExecStartPre=/bin/bash -c if [ ! "$DISABLE_ZONE_CHECKING" == "yes" ]; then /usr/sbin/named-checkconf -z "$NAMEDCONF"; else echo "Checking o>
Main PID: 124 (named)
Tasks: 7 (limit: 4915)
Memory: 56.6M
CGroup: /machine.slice/libpod-85f9421313e21d95745a04b15adc67749a39ebce96087a78e0e83db7ef6f3b16.scope/system.slice/named.service
└─124 /usr/sbin/named -u named -c /etc/namedb/named.conf
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: none:104: 'max-cache-size 90%' - setting to 10699MB (out of 11888MB)
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: configuring command channel from '/etc/rndc.key'
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: command channel listening on 127.0.0.1#953
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: configuring command channel from '/etc/rndc.key'
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: command channel listening on ::1#953
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: managed-keys-zone: loaded serial 0
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: zone example.com/IN: loaded serial 1001
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: all zones loaded
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: running
Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 systemd[1]: Started Berkeley Internet Name Domain (DNS).
- Query the SOA record from the new DNS-Server, check the flags to see that the answer is authoritative (AA-Flag)
[bind9]% dig @localhost soa example.com ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-10.P2.fc29 <<>> @localhost soa example.com ; (2 servers found) ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 13943 ;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: e2bfaaa71e139bacd7f36d815c0c3643b451622ab4174331 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;example.com. IN SOA ;; ANSWER SECTION: example.com. 3600 IN SOA dns.example.com. hostmaster.example.com. 1001 7200 1800 3542400 3600 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: ::1#53(::1) ;; WHEN: Sat Dec 08 21:23:15 UTC 2018 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 119
5.13.3 Dynamic DNS updates from Kea DHCP
- Work on the Kea DHCP Server machine
[host]% enter kea-server
- Create a configuration file for the
kea-dhcp-ddnsdaemon in/etc/kea/kea-dhcp-ddns.conf(writing domain names in full qualified format, including the "." at the end, is very important!):
{
"DhcpDdns": {
"ip-address": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 53001,
"dns-server-timeout": 100,
"ncr-protocol": "UDP",
"ncr-format": "JSON",
"tsig-keys": [],
"forward-ddns": {
"ddns-domains": [
{
"name": "example.com.",
"key-name": "",
"dns-servers": [
{
"hostname": "",
"ip-address": "100.64.53.1",
"port": 53
}
]
}
]
},
"reverse-ddns": {
"ddns-domains": []
},
"loggers": [
{
"name": "kea-dhcp-ddns",
"severity": "INFO",
"output_options": [
{
"output": "/var/log/kea/kea-dhcp-ddns.log"
}
]
}
]
}
}
- Test the configuration file
[kea-server]% kea-dhcp-ddns -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp-ddns.conf 2018-12-08 21:33:17.546 INFO [kea-dhcp-ddns.dctl/52] DCTL_CONFIG_CHECK_COMPLETE server has completed configuration check: listening on 127.0.0.1, port 53001, using UDP, result: success(0), text=Configuration seems sane.
- Start the Kea DHCP-DDNS (D2) server
[kea-server]% systemctl start kea-dhcp-ddns
[kea-server]% systemctl status kea-dhcp-ddns
● kea-dhcp-ddns.service - Kea DHCP-DDNS Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kea-dhcp-ddns.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2018-12-08 21:34:07 UTC; 4s ago
Docs: man:kea-dhcp-ddns(8)
Main PID: 55 (kea-dhcp-ddns)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
Memory: 1.8M
CGroup: /machine.slice/libpod-e96af203d05ac37853f65c7a93ffdbf87d509873172b7bab5abae1505f6a2c9b.scope/system.slice/kea-dhcp-ddns.service
└─55 /usr/sbin/kea-dhcp-ddns -c /etc/kea/kea-dhcp-ddns.conf
Dec 08 21:34:07 e96af203d05a systemd[1]: Started Kea DHCP-DDNS Server.
Dec 08 21:34:07 e96af203d05a kea-dhcp-ddns[55]: 2018-12-08 21:34:07.445 INFO [kea-dhcp-ddns.dctl/55] DCTL_STARTING DhcpDdns starting, pid: 55, version: 1>
Dec 08 21:34:07 e96af203d05a kea-dhcp-ddns[55]: 2018-12-08 21:34:07.446 INFO [kea-dhcp-ddns.dctl/55] DCTL_CONFIG_COMPLETE server has completed configurat>
Dec 08 21:34:07 e96af203d05a kea-dhcp-ddns[55]: 2018-12-08 21:34:07.446 INFO [kea-dhcp-ddns.dhcpddns/55] DHCP_DDNS_STARTED Kea DHCP-DDNS server version 1>
- In the
kea-dhcp4configuration file, revert back from PostgreSQL backend to the memfile backend for lease storage (because in this lab we do not have the database running)"lease-database": { "type": "memfile", "lfc-interval": 3600 }, - Enable DDNS in the
kea-dhcp4.confconfiguration file
{
"Dhcp4": {
"ddns-replace-client-name": "always",
"ddns-generated-prefix": "host",
"ddns-qualifying-suffix": "example.com.",
"dhcp-ddns": {
"enable-updates": true
},
[...]
- Test the configuration and restart the Kea DHCP server
- Monitor the Kea-DHCP-DDNS logfile
[kea-server]% tail -f /var/log/kea/kea-dhcp-ddns.log
- Start the relay-agent on the
relaycontainer[relay]% dhcrelay -id relay1-eth0 -id relay2-eth0 -iu relay3-eth0 -d 100.64.0.1
- Request a lease from
clientAandclientB. Observe the Kea-DHCP-DDNS logfile:
2025-11-09 12:57:06.382 INFO [kea-dhcp-ddns.dhcpddns/204.140027067733952] DHCP_DDNS_STARTED Kea DHCP-DDNS server version 3.0.2 started 2025-11-09 12:59:25.141 INFO [kea-dhcp-ddns.d2-to-dns/204.140027067733952] DHCP_DDNS_ADD_SUCCEEDED DHCP_DDNS Request ID 000001A6C9ECBFCADEC5EFD0831D340B864C96484AA0A2B4FE9B526085A7CCA57D87B4: successfully added the DNS mapping addition for this request: Type: 0 (CHG_ADD) Forward Change: yes Reverse Change: no FQDN: [host-192-0-2-100.example.com.] IP Address: [192.0.2.100] DHCID: [000001A6C9ECBFCADEC5EFD0831D340B864C96484AA0A2B4FE9B526085A7CCA57D87B4] Lease Expires On: 20251109131925 Lease Length: 1200 Conflict Resolution Mode: check-with-dhcid
- Log on the BIND 9 DNS-Server
# journalctl -fu named -- Logs begin at Sat 2018-12-08 21:07:04 UTC. -- Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: command channel listening on 127.0.0.1#953 Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: configuring command channel from '/etc/rndc.key' Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: command channel listening on ::1#953 Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: managed-keys-zone: loaded serial 0 Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: zone example.com/IN: loaded serial 1001 Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: all zones loaded Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 named[124]: running Dec 08 21:21:31 85f9421313e2 systemd[1]: Started Berkeley Internet Name Domain (DNS). Dec 08 21:51:47 85f9421313e2 named[124]: received control channel command 'sync' Dec 08 21:51:47 85f9421313e2 named[124]: dumping all zones: success Dec 08 21:53:49 85f9421313e2 named[124]: client @0x7f9a9c11e0b0 100.64.0.1#54788: updating zone 'example.com/IN': adding an RR at 'host-192-0-2-100.example.com' A 192.0.2.100 Dec 08 21:53:49 85f9421313e2 named[124]: client @0x7f9a9c11e0b0 100.64.0.1#54788: updating zone 'example.com/IN': adding an RR at 'host-192-0-2-100.example.com' DHCID AAEBkArIOOyXG4k9EcZV+7nh6DQ0iMsIAfNbdKZMqUJMmW4=
- Inspect updated zonefile on the BIND 9 DNS-Server
[bind9]% rndc sync
[bind9]% cat /etc/namedb/example.com
$ORIGIN .
$TTL 3600 ; 1 hour
example.com IN SOA dns.example.com. hostmaster.example.com. (
1003 ; serial
7200 ; refresh (2 hours)
1800 ; retry (30 minutes)
3542400 ; expire (5 weeks 6 days)
3600 ; minimum (1 hour)
)
NS dns.example.com.
$ORIGIN example.com.
dns A 100.64.53.1
host-192-0-2-100 A 192.0.2.100
DHCID ( AAEBkArIOOyXG4k9EcZV+7nh6DQ0iMsIAfNbdKZMqUJM
mW4= ) ; 1 1 32
host-198-51-100-50 A 198.51.100.50
DHCID ( AAEBCI5Fy5lEJYJbJcRaLLKHNUVpTN5HyOU8C/1Ijobh
CjM= ) ; 1 1 32
5.13.4 Change Hostname processing (optional exercise)
- In the configuration example above, the clients hostname will
always be replaced with an generated one. Change the setting
ddns-replace-client-namefromalwaystowhen-presentorwhen-not-present - Try the
dhclientparameter-H hostnameand-F hostname.domain.tldand see which DNS names are generated and updated by Kea DHCP
5.13.5 Securing DDNS with TSIG
- Operating DDNS with authentication based on IP-Adresses is insecure. In production environments, DDNS should be authenticated with TSIG
- In this exercise we change the previous DDNS configuration to use TSIG keys
- Generate a TSIG key
- On the BIND 9 DNS server machine we generate a TSIG key with the
name
kea-ddns
[bind9]% tsig-keygen kea-ddns key "kea-ddns" { algorithm hmac-sha256; secret "iSi6Z2aXlX3AkoWCORnUCUHb80H0x14vI7PaCGL66Co="; };- copy this information at the beginning of the BIND 9 configuration
file
named.conf
key "kea-ddns" { algorithm hmac-sha256; secret "iSi6Z2aXlX3AkoWCORnUCUHb80H0x14vI7PaCGL66Co="; }; options { [...]- Change the zone definition for
example.comto authenticate dynamic DNS update with the TSIG key:
[...] zone "example.com" { type master; allow-update { key "kea-ddns"; }; file "example.com"; };- Check the configuration and reload the BIND 9 DNS-Server
[bind9]% named-checkconf -z /etc/namedb/named.conf zone example.com/IN: loaded serial 1003 [bind9]% rndc reload server reload successful [bind9]% journalctl -fu named
- On the BIND 9 DNS server machine we generate a TSIG key with the
name
- Change the Kea DHCP-DDNS configuration
- On the Kea DHCP server, stop the
kea-dhcp4daemon, remove the lease-file (to trigger new DDNS updates) and start the service again
[kea-server]% systemctl stop kea-dhcp4 [kea-server]% rm /var/lib/kea/kea-leases* [kea-server]% systemctl start kea-dhcp4
- Add the TSIG key into the
tsig-keysarray in thekea-dhcp-ddns.conffile
{ "DhcpDdns": { "ip-address": "127.0.0.1", "port": 53001, "dns-server-timeout": 100, "ncr-protocol": "UDP", "ncr-format": "JSON", "tsig-keys": [ { "name": "kea-ddns", "algorithm": "HMAC-SHA256", "secret": "iSi6Z2aXlX3AkoWCORnUCUHb80H0x14vI7PaCGL66Co=" } ], "forward-ddns": { [...]- Add the name of the TSIG key to use in the
ddns-domainsblock
[...] "forward-ddns": { "ddns-domains": [ { "name": "example.com.", "key-name": "kea-ddns", "dns-servers": [ { "hostname": "", "ip-address": "100.64.53.1", "port": 53 } ] } ] }, [...]- Test the new configuration and restart
kea-dhcp-ddns
[kea-server]% kea-dhcp-ddns -t /etc/kea/kea-dhcp-ddns.conf [kea-server]% systemctl restart kea-dhcp-ddns
- Request a new lease from one of the clients and inspect the log outout on the BIND 9 DNS server
Dec 08 22:23:56 85f9421313e2 named[124]: client @0x7f9a9c101170 100.64.0.1#50032/key kea-ddns: signer "kea-ddns" approved Dec 08 22:23:56 85f9421313e2 named[124]: client @0x7f9a9c101170 100.64.0.1#50032/key kea-ddns: updating zone 'example.com/IN': deleting rrset at 'host-198-51-100-50.example.com' A Dec 08 22:23:56 85f9421313e2 named[124]: client @0x7f9a9c101170 100.64.0.1#50032/key kea-ddns: updating zone 'example.com/IN': adding an RR at 'host-198-51-100-50.example.com' A 198.51.100.50
- On the Kea DHCP server, stop the
5.13.6 Clean Up Lab04
- Exit from the
kea-server,relay,bind9clientAandclientBcontainer - Execute the script
./stopand./cleanin/root/lab/lab04
5.14 LAB05 - Kea-DHCP Failover Cluster
5.14.1 Preparing the Lab
- Change into the
/root/lab/lab05directory and execute the./runscript to prepare the lab environment - Enter the
kea-server1and check the Kea server version number
[host]% enter kea-server1 [kea-server]% kea-dhcp4 -V 3.0.2 (3.0.2 (tarball)) premium: no linked with: - log4cplus 2.1.2 - OpenSSL 3.5.4 30 Sep 2025 lease backends: - Memfile backend 3.0
5.14.2 Configuring Kea DHCP for Hot-Standby Mode
- Add a HA Standby configuration to
kea-server1in the file/etc/kea/kea-dhcp4.conf. The Hook-Librarydhcp_lease_cmdsis required for the HA Module (it uses the REST API functions defined in this hook):
"Dhcp4": {
[...]
"hooks-libraries": [
{
"library": "/usr/lib64/kea/hooks/libdhcp_lease_cmds.so",
"parameters": { }
},
{
"library": "/usr/lib64/kea/hooks/libdhcp_ha.so",
"parameters": {
"high-availability": [ {
"this-server-name": "server1",
"mode": "hot-standby",
"heartbeat-delay": 10000, # miliseconds
"max-response-delay": 20000, # miliseconds
"max-ack-delay": 5000, # miliseconds
"max-unacked-clients": 0, # immediate partner down
"peers": [
{
"name": "server1",
"url": "http://100.64.0.1:9098/",
"role": "primary",
"auto-failover": true
},
{
"name": "server2",
"url": "http://100.64.1.1:9098/",
"role": "standby",
"auto-failover": true
}
]
} ]
}
}
],
[...]
- Change the Interface name in the Kea-DHCP4 Module from
server-eth0toserver1-eth0 - Test the Kea DHCP4 server configuration and start the Kea server
- Start monitoring the Kea DHCP4 log file
[kea-server1]% tail -f /var/log/kea/kea-dhcp4.log
- Copy the configuration from kea-server1 to kea-server2 (on the VM host)
[host]% cp /root/lab/conf/kea-dhcp4.conf /root/lab/conf2/ [host]% cp /root/lab/conf/kea-ctrl-agent.conf /root/lab/conf2/
- On a different terminal, enter
kea-server2
[host]% enter kea-server2
- Change the
this-server-nameconfiguration option in the Kea DHCP4 server configuration file to the textserver2 - Change the Interface name in the Kea-DHCP4 Module configuration
from
server1-eth0toserver2-eth0 - Test the configuration for the Kea DHCP4 server, start the server and check that the service has been started
[kea-server2]% systemctl start kea-dhcp4 [kea-server2]% systemctl status kea-dhcp4
- Start monitoring the Kea DHCP4 log file
[kea-server2]% tail -f /var/log/kea/kea-dhcp4.log
- You should see the HA protocol to sync and to start sending heartbeat messages between the two servers
5.14.3 DHCP-Relay-Agent for a DHCP-Cluster
- On a different terminal, enter the
relaymachine - Start the DHCP-Relay to send the requests from clients to both Kea DHCP4 servers
[relay]% dhcrelay -id relay1-eth0 -id relay2-eth0 -iu relay3-eth0 -iu relay4-eth0 \
-d 100.64.0.1 100.64.1.1
5.14.4 Request a lease
- Request a lease from a client. This lease should come from
kea-server1and the lease should be synced tokea-server2(look into the lease file on disk)
[client1]% dhclient -v client1-eth0
5.14.5 Test the HA function
- Stop the process
kea-dhcp4on the machinekea-server1
[kea-server1]% systemctl stop kea-dhcp4
- The log messages on
kea-server2should indicate thepartner-downstate - Requests from
clientAshould now served after 5000ms fromkea-server2 - Start the process
kea-dhcp4onkea-server1. Watch the lease-database synchronize, request a lease from a client, that client should now be served fromkea-server1again.
[kea-server1]% systemctl start kea-dhcp4
6 Lab-Setup source code
- The Lab setup code for the virtual machines used in this training can be found under a permissive license at https://github.com/cstrotm/kea-dhcp-training-lab